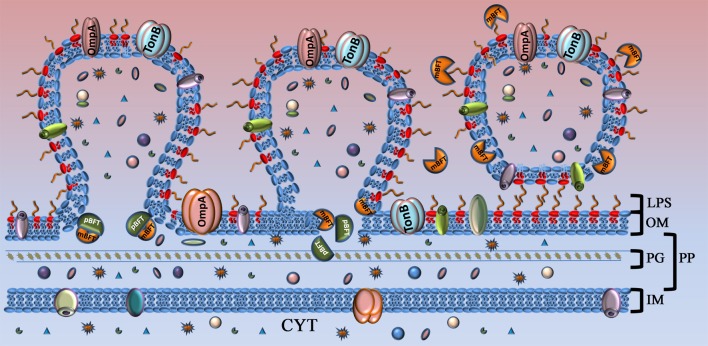
Figure 8.
Model of toxin capture during vesicle formation. Toxin is shown as complex of two subunits. Part of the toxin that will be processed (pBFT) and degraded is colored in dark green. Active part of the toxin (mBFT) colored in orange. OM, outer membrane; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PG, peptidoglycan; PP, periplasm; IM, inner membrane; CYT, cytoplasma. At the beginning of vesicle formation, the major part of the toxin is not processed and could be found in membrane. During vesicle formation toxin could be processed by B. fragilis cysteine protease. Free grooves, located on the protein surface, formed during toxin processing interact with fatty acid residues of outer membrane lipids by hydrophobic interaction. Toxin promoted to the OMV surface where it interact with LPS. Incorporated or tightly binding toxin delivered to the target cell by OMVs.