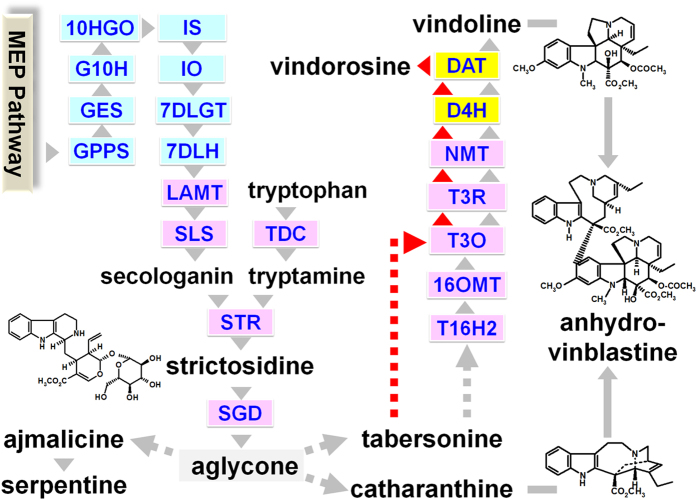
Figure 1. Biosynthetic pathway of MIAs in C. roseus.
Simplified representation of the MIA biosynthesis in C. roseus leaves highlighting the cellular organization of the pathway in internal phloem associated parenchyma (blue rectangles), epidermis (pink rectangles), laticifers/idioblastes (yellow rectangles). Known single enzymatic steps are indicated by grey/red arrowheads and abbreviation of enzyme names. Broken grey/red arrows indicate unknown enzymatic steps. Conversion of tabersonine may occur in two ways to generate vindorosine (red arrows) or vindoline (grey). MEP, methyl-D-erythritol phosphate; GPPS, geranyl diphosphate synthase; GES, geraniol synthase; G10H, geraniol 10-hydroxylase; 10HGO, 10-hydroxygeraniol oxidoreductase; IO, iridoid oxidase; IS, iridoid synthase; 7DLGT, 7-deoxyloganetic acid glucosyltransferase; 7DLH, 7-deoxyloganic acid 7-hydroxylase; LAMT, loganic acid O-methyltransferase; SLS, secologanin synthase; TDC, tryptophan decarboxylase; STR, strictosidine synthase; SGD, strictosidine β-glucosidase; T16H2, tabersonine 16-hydroxylase 2; 16OMT, 16-hydroxytabersonine O-methyltransferase; T3O, tabersonine 3-oxidase; T3R, tabersonine 3-reductase; NMT, 16-methoxy-2,3-dihydrotabersonine N-methyltransferase; D4H, desacetoxyvindoline 4-hydroxylase; DAT, deacetylvindoline 4-O-acetyltransferase.