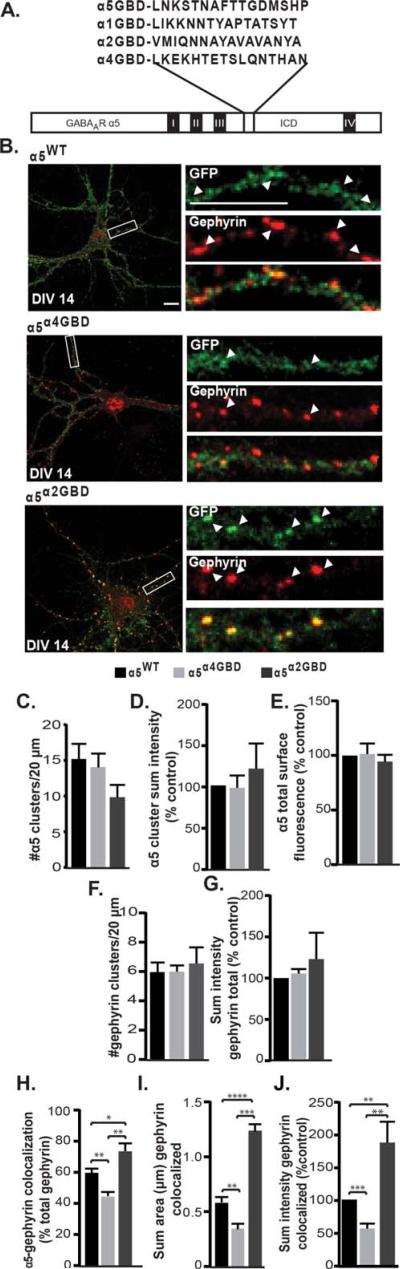
Figure 3.
Disruption of the gephyrin binding domain in the α5 subunit decreases its association with gephyrin. (A) Alignment of homologous regions of the gephyrin binding domain (GBD) of different alpha subunits, and construction of the α5α4GBD and α5α2GBD chimeras. (B) DIV 14 neurons expressing the α5WT, α5α4GBD, or α5α2GBD constructs were fixed and stained for surface GABAAR (anti-GFP, green) and gephyrin (red). (C–E) In transfected neurons, there was no significant difference in the total number of α5 clusters per 20 μm, the total sum intensity of α5 clusters, or the total α5 surface fluorescence. (F and G) There was no significant difference in the total number of gephyrin clusters per 20 μm or the overall sum intensity of gephyrin between groups. (H) Swapping the α5 GBD for the α4 GBD significantly decreased colocalization of the α5 subunit with gephyrin, while exchanging the α5 GBD for the α2 GBD significantly increased gephyrin colocalization (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (I and J) The sum area and sum intensity of gephyrin clusters colocalized with tagged GABAAR was significantly decreased in neurons transfected with the α5α4GBD compared to control, while neurons transfected with α5α2GBD showed a significant increase in sum area and sum intensity of colocalized gephyrin clusters (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001).