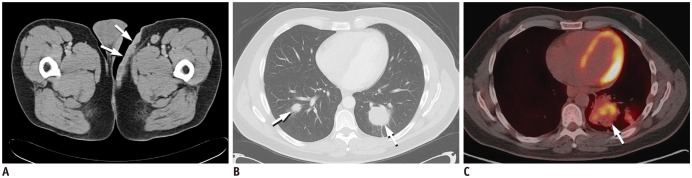
Fig. 2. Contrast-enhanced CT and 18FDG PET-CT in patient with transformed cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Axial contrast-enhanced CT image (A) demonstrates diffuse skin thickening in left groin (arrows), which resolved following treatment with radiation, phototherapy, and Targretin (not shown). Unfortunately, on subsequent restaging contrast-enhanced chest CT (B), patient developed bilateral pulmonary masses (arrows), which were biopsy proven cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. As seen on axial fused PET-CT image (C), pulmonary lesions increased in size and number despite treatment with cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and prednisone (CHOP) regimen (arrow), pralatrexate, gemcitabine, Ontak, allogenic stem cell transplant, and palliative radiation and patient eventually expired from pulmonary complications. FDG = flourodeoxyglucose, PET = positron emission tomography