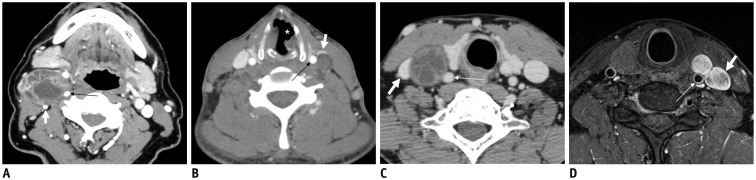
Fig. 16. Axial CT (A-C) and axial contrast-enhanced fat-suppressed T1-weighted (D) images in four different patients with vagal schwannomas (long arrows) demonstrating anatomical variations of vagus nerve within carotid sheath displacing internal jugular vein (short arrows) and internal carotid artery (thin arrow on A) or common carotid artery (thin arrows on B-D) in different directions.
Note vocal-cord atrophy (asterisk) caused by vagus nerve palsy on ipsilateral side in B.