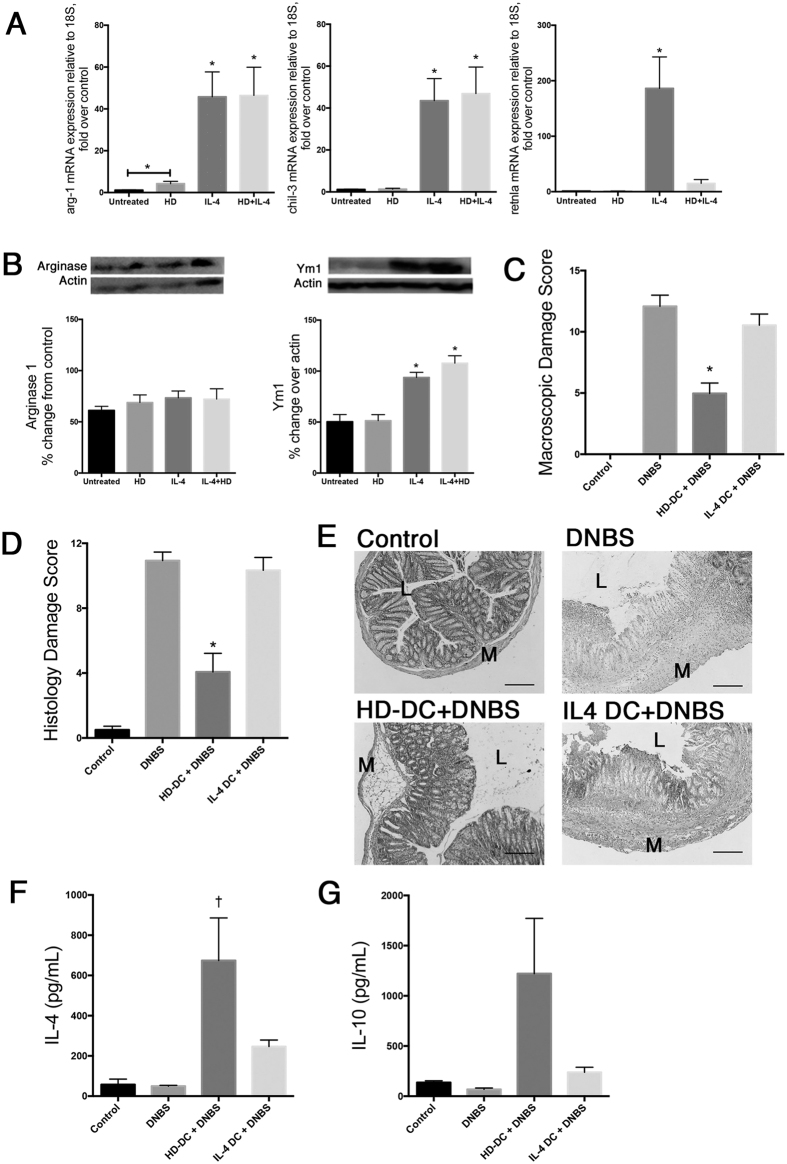
Figure 6. IL-4 alternatively activated DCs are not able to suppress colitis in recipients.
Levels of arg-1, chil3 (Ym1), and retnla mRNA expression (A; n = 6–10 from 3 experiments) and arginase-1 and Ym1 protein expression (B; n = 6 from 2 experiments), with representative western blots, in untreated DCs, and DCs treated with HD antigen (100 μg/mL) and/or IL-4 (20 ng/mL) for 24 h. Data are shown as mean ± SEM; Repeated one-way ANOVA with Dunn’s post-test; *p ≤ 0.05. For additional experiments, Balb/c mice were given 106 HD-DC (100 μg/mL) or IL-4 alternatively activated (AA) DCs (20 ng/mL) ip. 48 h prior to DNBS (3 mg, i.r.) challenge. Mice were necropsied and assessed 72 h later via (C) macroscopic damage score and (D) histological damage score, with Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn’s post-test. (E) Representative micrographs of H&E stained cross-sections of colonic tissue: L; lumen; M: muscle; scale bar 300 μm). Splenocytes were isolated (5 × 106), stimulated with conA (2 μg/mL, 48 h) and supernatants examined for levels of IL-4 (F) and IL-10 (G) by ELISA, and analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test. Data are shown as mean ± SEM and are pooled from two independent experiments; n = 6–8 mice/group; p < 0.05: *compared to DNBS, †compared to all groups.