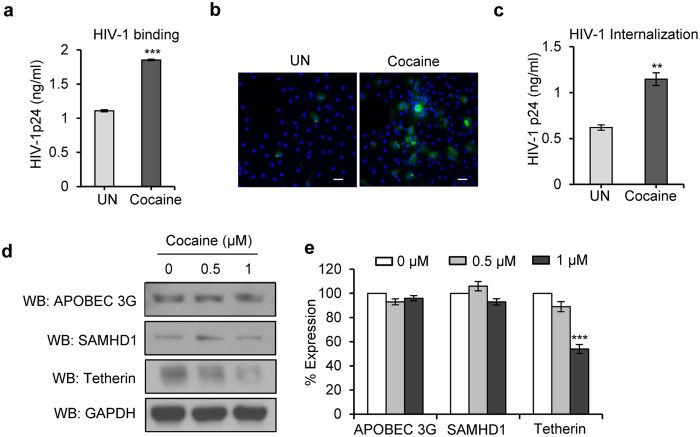
Figure 2. Cocaine increases HIV-1 BaL binding and internalization in DCs.
(a) For virus binding studies, DCs were untreated or pre-treated with cocaine (1 μM) at 37 °C for 2 hours then incubated with HIV-1 BaL for 2 hours at 4 °C, and the cell lysates were analyzed for HIV-1 p24 levels. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments (***p ≤ 0.001). (b,c) Cocaine (1 μM) pre-treated or untreated DCs were incubated with HIV-1 BaL for 4 hours at 37 °C. The cells were incubated with trypsin, washed and analyzed under confocal microscopy (Green = HIV-1 p24; Blue = DAPI; Scale bar = 10 μm) or cell lysates were quantitated for p24 titer by using ELISA. Data represent the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments for untreated cells vs. cells treated with cocaine (**p ≤ 0.01, 2-tailed t-test). (d) Western blot analysis of APOBEC3G, SAMHD1 and tetherin in DCs treated with cocaine (0–1 μM) for 24 hours. GAPDH served as a loading control. (e) Quantitative analysis of Western blots of APOBEC3G, SAMHD1 and tetherin in DCs treated with cocaine (0–1 μM) for 24 hours. The band intensity in each lane was determined by densitometry. The fold change was determined by calculating the value of untreated (0) lane as 1. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments (***p ≤ 0.001, 2-tailed t-test).