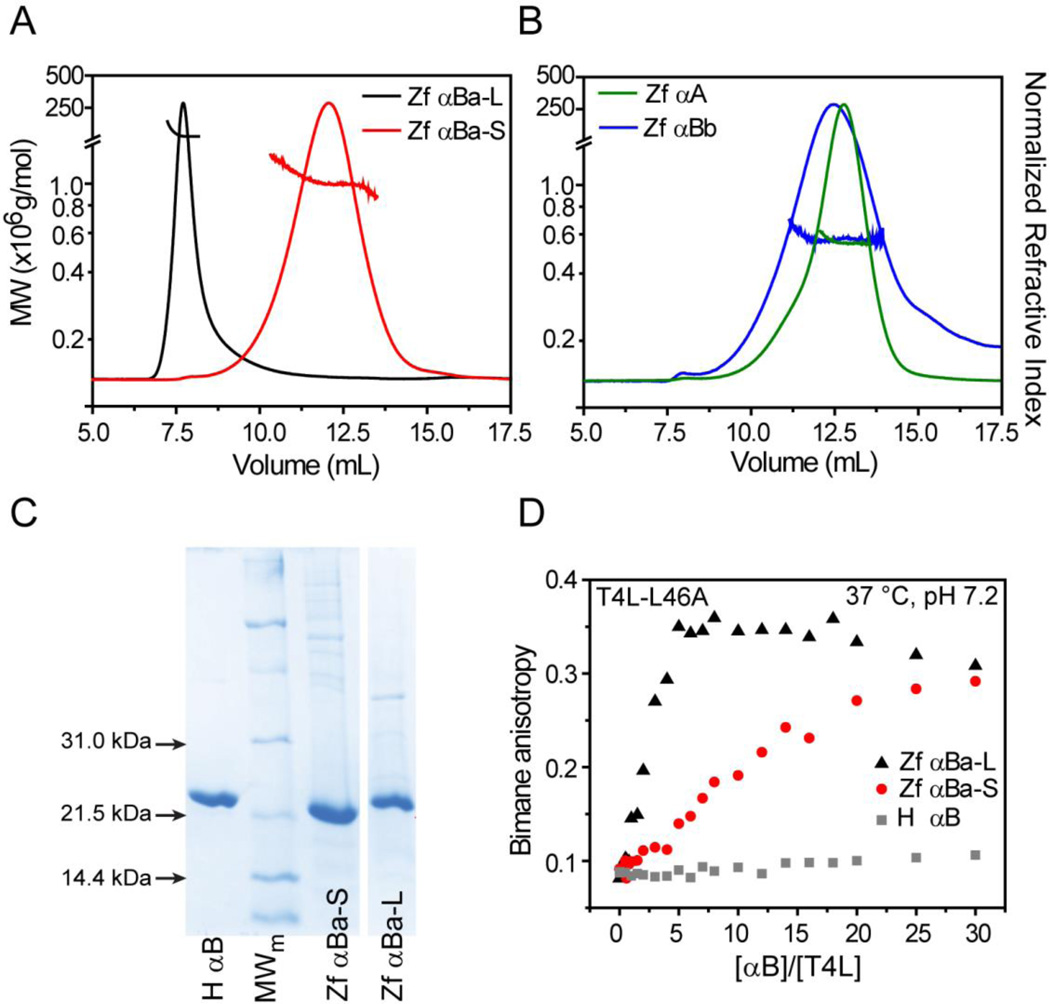
Figure 1.
Oligomeric properties of zebrafish α-crystallins. (A) Purification of αBa isolated two populations with distinct chromatographic behaviors and MALS profiles, revealing average molecular weights greater than 1 × 106 g mol−1. (B) In contrast, αA and αBb formed smaller oligomers of similar mass as reported in Table 2. (C) SDS-PAGE confirmed that αBa and αBb oligomers were constructed from subunit monomers of comparable molecular weight and purity. (D) Titration of a constant concentration of bimane-labeled T4L (3µM for αBa-L and αBa-S, 5µM for human αB) with α-crystallin increases bimane anisotropy, indicative of complex formation. Parallel to the differences in oligomer size, αBa-L demonstrated elevated binding activity to the T4L-L46A substrate relative to αBa-S. In contrast, very little binding of this T4L mutant by human αB was detected.