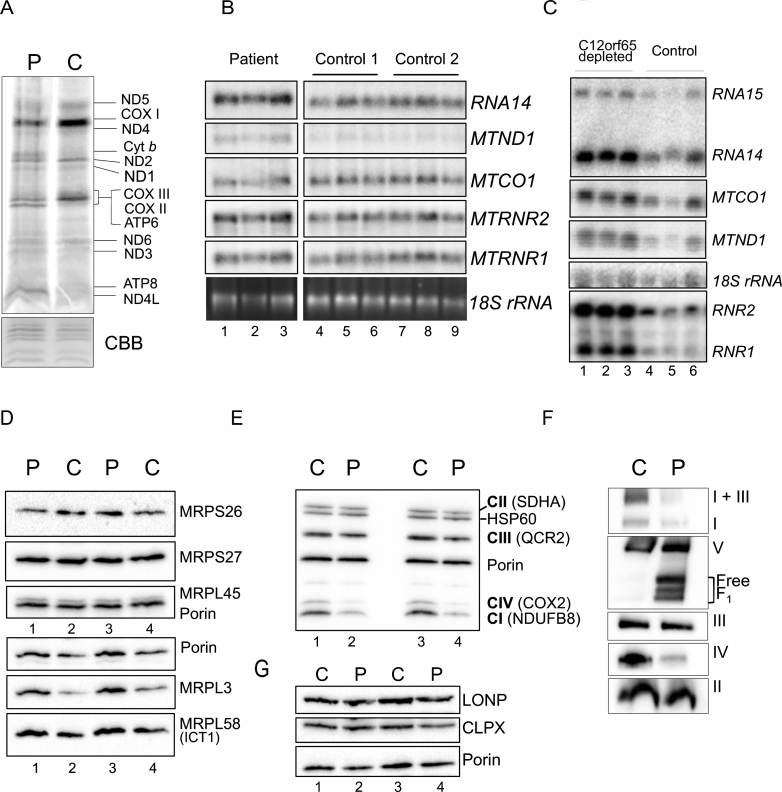
Fig.4.
Gene expression analyses of OXPHOS components and related proteins. A. Intramitochondrial protein synthesis was measured in cell lysates by incorporation of 35S-methionine and cysteine into fibroblasts derived from patient (P) or control (C). The relative positions of the mt-proteins are indicated. Protein loading was confirmed by Coomassie blue (CBB) staining of the gel. B. Northern blot analysis was performed on patient and control RNA (4 μg) to quantify the steady state levels of the RNA species indicated. The cytosolic 18 S rRNA was used as a loading control. C. Similar analyses were performed on human kidney cells (HEK293) following 6 days siRNA mediated depletion of C12orf65 (lanes 1–3), or a non-targetting control siRNA (lanes 4–6) reflecting 3 experimental repeats. The cytosolic 18 S rRNA was used a loading control. Westerns of patient and control mitochondrial lysates (12.5 μg) were separated by 12% SDS:PAGE to detect levels of mitoribosomal proteins (D), respiratory chain proteins (E) or mitochondrial proteases (G) using porin as a loading control. F. Assembly and integrity of the OXPHOS complexes was determined by blue native 4.5–16% gradient PAGE of mitochondrial lysates (25 μg) from patient and control. After transfer, Western blot analysis was used to visualize all OXPHOS complexes with subunit specific antibodies as follows: complex I (NDUFA9), complex III (Core 2) and complex II (SDHA), complex IV (COX4) and complex V (α-subunit).