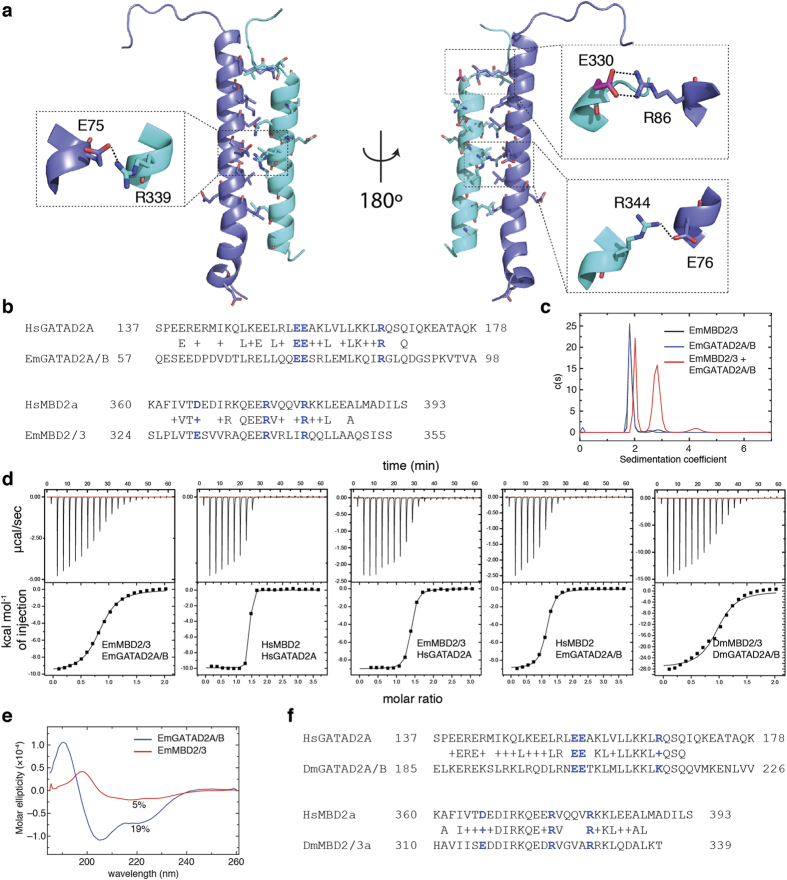
Figure 5. The coiled-coil interaction between EmMBD2/3 and EmGATAD2A/B.
(a) A cartoon diagram depicts the final frame from a 40ns molecular dynamics simulation of a model of the coiled-coil interaction between EmMBD2/3 (cyan) and EmGATAD2A/B (blue). The amino acids residues conserved between the human and E. muelleri complexes (shown in sticks) are primarily located at the interface between the proteins. Expanded views (dashed boxes) show preservation of three critical ionic and hydrogen bond interactions, with the only difference between species involving a conservative aspartate to glutamate (E330) change (highlighted in magenta). (b) Alignment of the coiled-coil domains shows relatively low overall identity but with conservation of critical ionic (blue) and interface residues. (c) Analytical ultracentrifugation sedimentation velocity analyses indicates that the isolated EmMBD2/3 (black) and EmGATAD2A/B (blue) are largely monomeric while a mixture of the two (red) sediments as a combination of monomeric and heterodimeric species. (d) Isothermal titration calorimetry shows that the EmMBD2/3:EmGATAD2A/B and DmMBD2/3:DmGATAD2A/B complexes bind with relatively low affinity as compared to HsMBD2:HsGATAD2A; whereas cross-species (Em:Hs) complexes bind with intermediate affinities. (e) Circular dichroism measurements show that the EmGATAD2A/B (blue) an EmMBD2/3 (red) domains have relatively low helical content in isolation. (f) Alignment of DmMBD2/3 and DmGATAD2A/B with human orthologs shows a higher degree of conservation as compared to sponge.