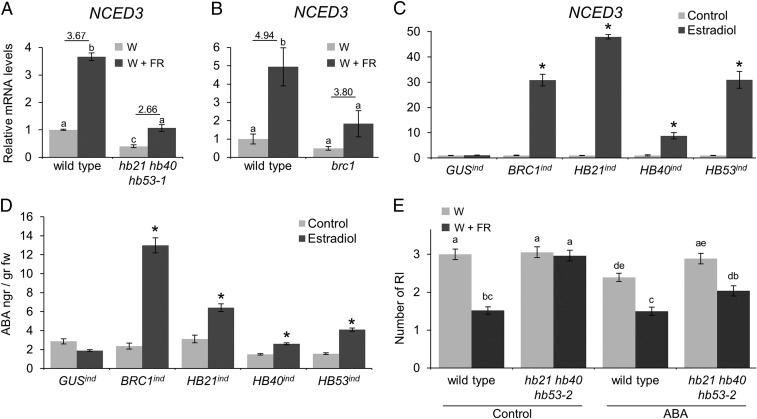
Fig. 4.
BRC1, HB21, HB40, and HB53 promote ABA accumulation via NCED3. (A and B) NCED3 mRNA levels analyzed by quantitative PCR measured in axillary buds of wild-type plants and hb21 hb40 hb53-1 mutants (A) and brc1 mutants (B) treated with W or W+FR light for 8 h. (C) NCED3 mRNA levels in 7-d-old GUSind, HA:BRC1ind, HA:HB21ind, HA:HB40ind, and HA:HB53ind seedlings after an 8-h treatment with 10 µM estradiol. (D) ABA levels measured in estradiol-treated seedlings of the genotypes in C. (E) Branching phenotype of wild-type and hb21 hb40 hb53-2 plants treated with W or W+FR light and 50 µM ABA or mock (control) for 2 wk after bolting (n = 28). Error bars show the SEM of three biological replicates. Asterisks show significant differences (P < 0.05; student’s t-test) between control and treated plants. Letters denote significant differences (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA) among means.