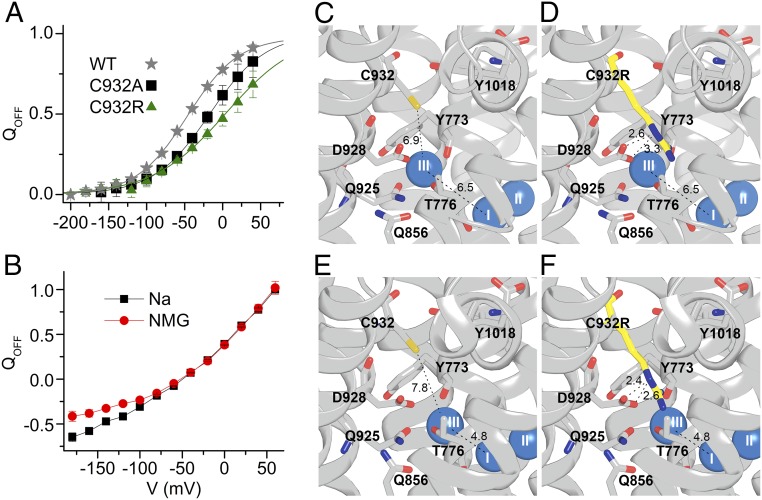
Fig. 6.
Binding of extracellular Na+ by C932R and structural interpretation. (A) Normalized Q-V relation for WT, C932A, and C932R (data in Fig. 5B). Data were fitted with the Boltzmann distribution (lines), giving parameters V0.5 (center of distribution) and k (slope factor) (17). Parameters from the best fit (in millivolts) were V0.5 = −46.4 ± 0.7, k = 33.8 ± 0.8 for WT; V0.5 = −17.0 ± 6.2, k = 36.6 ± 3.8 for C932A; and V0.5 = 4.3 ± 9.8, k = 48.2 ± 4.2 for C932R. QOFF, holding voltage. (B) Normalized Q-V for C932R measured in the presence and absence (NMG) of 125 mM external Na+. (C–F) Structures based on PDB ID code 3WGV, protomers A and B (chains C and A, respectively, in the PDB file), with C932 being replaced by arginine in D and F. Wild-type protomer B (C), C932R protomer B (D), wild-type protomer A (E), and C932R protomer A (F) are shown. Side views with the cytoplasmic side up are shown. The bound Na+ ions are shown as blue spheres. Broken lines with numbers indicate distances in angstroms.