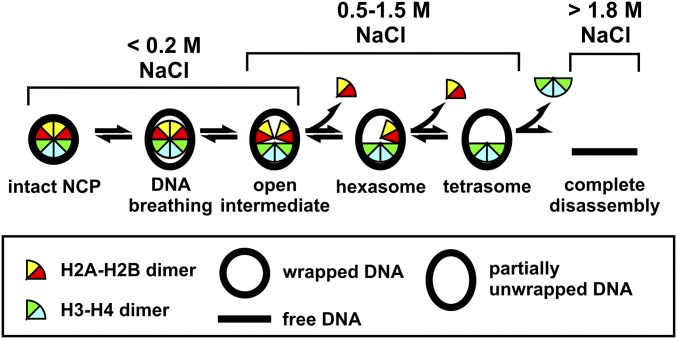
Fig. 1.
A schematic of NaCl-dependent disassembly for NCPs containing the 601-DNA (15), based on equilibrium studies ([NCP] ≥ 25 nM). At physiological ionic strength, NCP configurations reflect local dynamics [i.e., DNA breathing (6), and formation of an open intermediate (8)]. Above 0.5 M NaCl, H2A–H2B dimers begin to dissociate, allowing the formation of hexasomes and tetrasomes (23). Above 1.4 M NaCl, (H3–H4)2 tetramers begin to dissociate, allowing for complete disassembly (24). Although dimer dissociation is reversible, tetrasomes are the minimal configurations required to maintain a wrapped DNA structure.