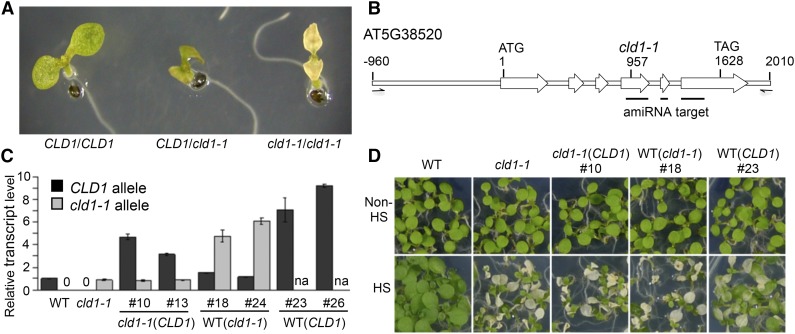
Figure 1.
cld1-1 Is a Semidominant Allele of AT5G38520 that Causes a Heat-Sensitive Phenotype.
(A) Phenotypes of 5-d-old Arabidopsis seedlings with homozygous or heterozygous cld1-1 allele after treatment at 40°C for 1 h (HS) plus 3-d recovery under normal growth condition. The representative seedlings showed nonbleaching (CLD1/CLD1), slow-bleaching (CLD1/cld1-1), and fast-bleaching (cld1-1/cld1-1) phenotypes. Without HS, the wild-type and mutant cotyledons were all green and are not shown here.
(B) Diagram of CLD1 gene between −960 to 2010 bp is shown with the translational start site (ATG) set as +1 and stop codon (TAG) at 1628. The white arrows indicate the exons. The mutation site in cld1-1 is indicated at position 957 with a G-to-A transition. The black lines underneath indicate the target regions of artificial microRNA. The half arrows, which are not to scale, indicate the forward and reverse primers for PCR amplification of CLD1 genomic DNA for complementation test.
(C) Relative CLD1 or cld1-1 transcript levels in 5-d-old seedlings of different transgenic lines normalized to that of the wild type or cld1-1 mutant, respectively. Data are means ± sd of three replicates. na, not analyzed.
(D) Phenotyping of representative transgenic lines with or without HS treatment. The transgenic lines are labeled as cld1-1(CLD1), cld1-1 transformed with ectopic CLD1 genomic DNA; WT(cld1-1), the wild type transformed with ectopic cld1-1 genomic DNA; WT(CLD1), the wild type transformed with ectopic CLD1 genomic DNA. Numbers after the symbol “#” indicate the line designations derived from independent transformation events. Seedlings in the same row were grown on the same plate and reorganized for presentation.