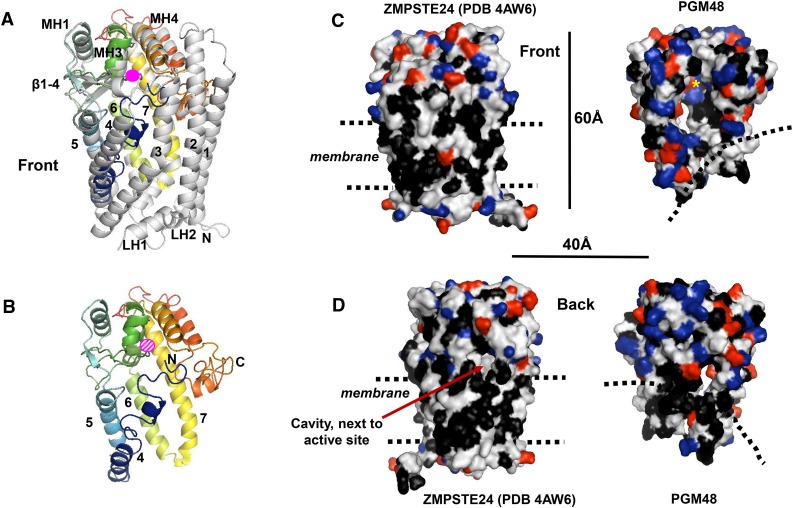
Figure 3.
3D Protein Structural Model for PGM48 and Predicted Interface with the PG Monolayer.
The 3D protein structural model of PGM48 was generated with i-TASSER (Yang et al., 2015) using the predicted mature PGM48 sequence (residues 48 to 344). The top scoring i-TASSER model for PGM48 had a C-score of −0.98 (C-scores range from −5 [poorest] to 2 [best]) and estimated TM score of 0.59 ± 0.14. Analysis of PGM48 protein model using ProSA (Wiederstein and Sippl, 2007) gave a Z-score of −3.73, which is well within the range of scores found for protein structures of this molecular weight generated by crystallography and NMR. The protein model matched most closely to the 3.8-Å structure PDB 4AW6 of the M48 protein STE24 from humans (Quigley et al., 2013). Images were generated with PyMol Version 1.7.4 software (Schrödinger).
(A) Front view of STE24 structure (4AW6) in gray overlaid with the colored modeled PGM48. PGM48 is colored in rainbow from blue N terminus to red C terminus. The Zn metal ion is marked in pink (not to scale). The STE24 helices 1 to 7, lumenal helices (L1 to 3), and cytoplasmic helices (MH1, 3, and 4) are marked using the naming from Quigley et al. (2013). Helices 1, 2, 3, 7A, LH1, and LH2 are absent in the PGM48 model.
(B) Front view of the PGM48 model. Helices are numbered according to 4AW6, and the N and C termini are indicated; the position of the Zn ion is indicated in dashed pink.
(C) and (D) Side-by-side comparison of the structure 4AW6 of STE24 and the PGM48 model using a surface representation. Amino acid side chains are colored in black for hydrophobic residues (Leu, Ile, Val, Phe, Trp, and Ala), red for acidic residues (Glu and Asp), and blue for basic residues (Lys, Arg, and His). Dimensions (in Å) and approximate location of the ER/nuclear membrane lipid bilayer (STE24) and postulated PG lipid surface (PGM48) (dashed lines) are indicated.