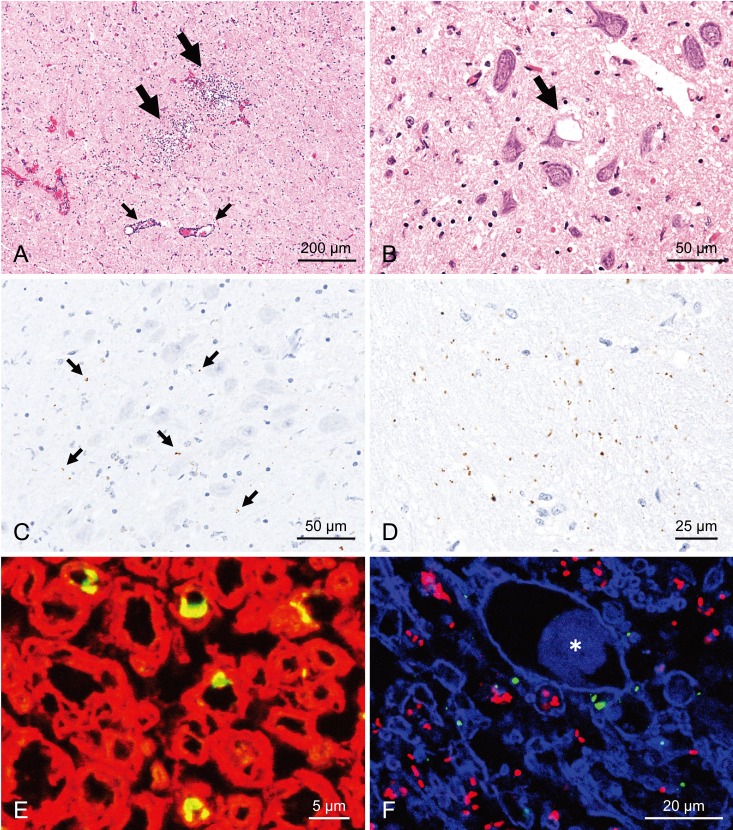
Fig. 2.
Histopathological and immunohistochemical features in the medulla oblongata at the obex of the Japanese atypical scrapie sheep. A, Focal microabscesses composed of neutrophils with some macrophages (large arrows) and perivascular mononuclear cell cuffing (small arrow) at the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve. B, A single intraneuronal vacuole (arrow) in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (DMNV). C, Fine granular PrPSc immunolabeling with mAb T1 (arrows) in the neuropil of the DMNV. D, Fine granular to globular PrPSc immunolabeling with mAb T1 in the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve. E, Granular PrPSc at the ad-axonal location (yellow) in the white matter of the olivocerebellar tract. PrPSc (green; Alexa Fluor 488) and myelin sheath (red; Alexa Fluor 546) were labeled with mAb F99/97.6.1 and myelin basic protein (clone 12; Millipore, Billerica, MA, U.S.A.) and imaged by confocal microscopy (LSM 510; Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). F, Colocalization of PrPSc (green; Alexa Fluor 488) and Listeria monocytogenes (red; Alexa Fluor 546) in the necrotic lesion of the spinocerebellar tract by dual immunofluorescence with mAb F99/97.6.1 and an antibody to Listeria followed with TO-PRO-3 counterstaining (blue). Asterisk (*) indicates axonal swelling.