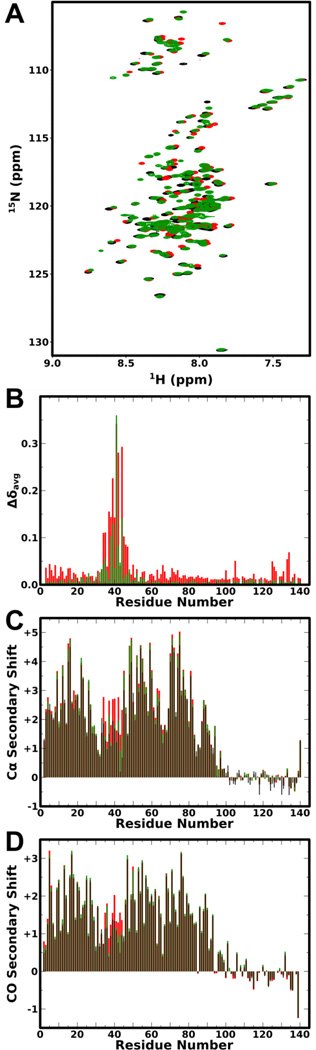
Figure 1. NMR analysis of the effect of Y39 phosphorylation on aSyn binding to SDS micelles.
A: 1H,15N-HSQC spectra of WT (black) aSyn, pY39 aSyn Y125F/Y133F (red), and aSyn Y39E (green) in the presence of SDS micelles. B: Plot of average amide chemical shift difference between pY39 aSyn Y125F/Y133F and WT aSyn (red) and between aSyn Y39E and WT aSyn (green) in the presence of SDS micelles versus residue number. C: Plot of Cα secondary shifts for unphosphorylated WT (black), pY39 aSyn Y125F/Y133F (red) and aSyn Y39E (green) in the presence of SDS micelles versus residue number. D: Plot of CO secondary shifts for unphosphorylated WT (black), pY39 aSyn Y125F/Y133F (red) and aSyn Y39E (green) in the presence of SDS micelles versus residue number. For panels C and D, positive and negative values indicate helical and extended structure, respectively.