Figure 1.
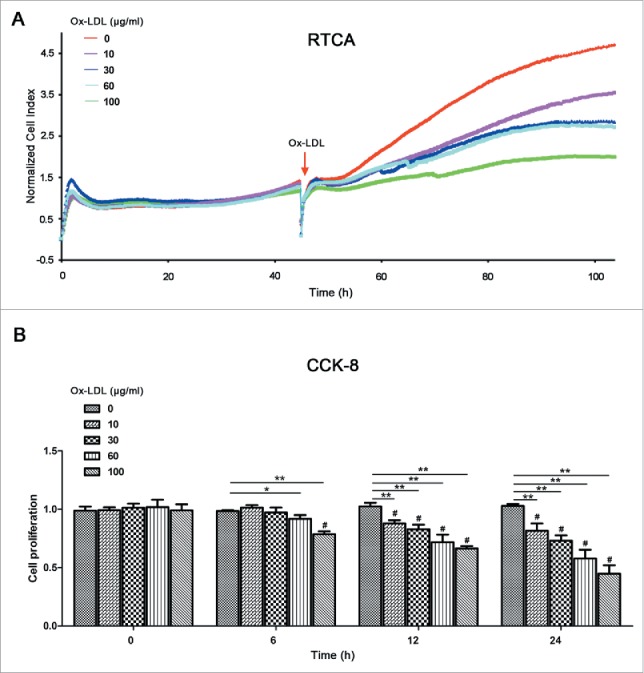
Ox-LDL treatment decreases EPC proliferative activity. (A) After seeding on E-plates for 48 h, EPCs were treated with different concentrations of ox-LDL (0, 10, 30, 60 or 100 μg/ml) respectively (red arrow) and monitored by RTCA. The normalized cell index indicated ox-LDL dose-dependently decreased EPC proliferation. Representative graphs were shown from 3 independent experiments. (B) CCK-8 results showed ox-LDL reduced EPC proliferative activity in dose- and time-dependent manners after 0, 6, 12 or 24 h ox-LDL exposure at a series of concentrations (0, 10, 30, 60 or 100 μg/ml). (Cells were isolated from 3 rats for 1 experiment and 3 independent experiments were performed; mean + SD; #P < 0.01, compared with 0 h within the same concentration group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with 0 μg/ml `ox-LDL in the same time of exposure).
