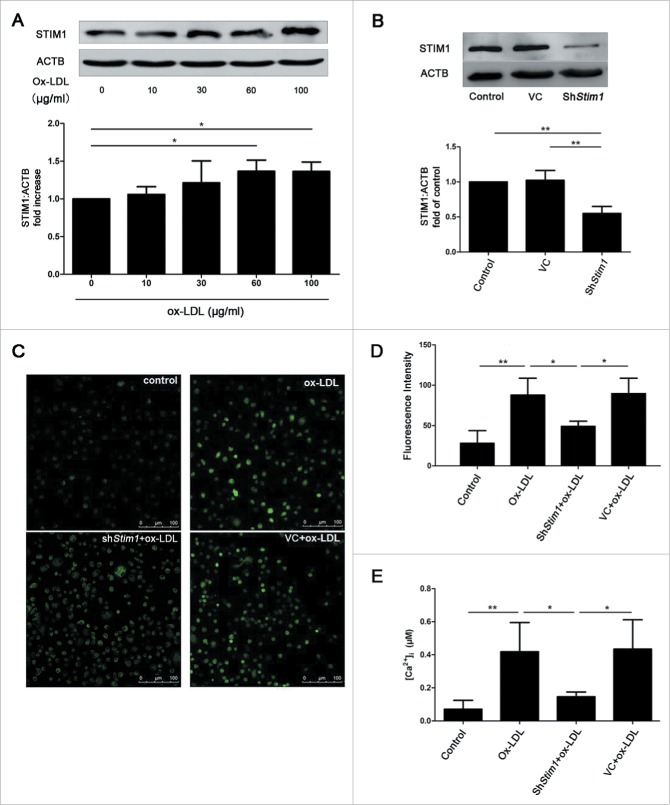
Figure 5.
Ox-LDL upregulates STIM1 and increases [Ca2+]i. (A) Representative western blots for detection of STIM1 after treated with ox-LDL (0, 10, 30, 60 or 100 μg/ml) respectively for 12 h and quantitative analysis demonstrated that ox-LDL significantly increased the protein level of STIM1 at the concentration of 60 or 100 μg/ml. (B) Representative western blots and quantitative analysis showed shRNA targeting Stim1 (shStim1) effectively silenced STIM1 protein expression after 72 h infection. (C) EPCs were infected by shStim1 followed by ox-LDL (60 μg/ml) for 12 h, then examined with the fluorescent dye fluo3 under an LCSM. The representative images showed the fluorescence intensity in different groups. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Quantitative analysis showed that the fluorescence intensity in ox-LDL and VC+ox-LDL groups were significantly stronger than control and shStim1+ox-LDL groups. (Control: n = 97 cells, Ox-LDL: n = 91 cells, ShStim1+ox-LDL: n = 94 cells, VC+ox-LDL: n = 97 cells). (E) The exact [Ca2+]i was calculated by the equation mentioned above, indicating that ox-LDL increased [Ca2+]i, silencing Stim1 reversed the increase elicited by ox-LDL. (Cells were isolated from 3 rats for 1 experiment and 3 independent experiments were performed, western blot results were normalized to the controls (given as 1-fold), mean + SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).