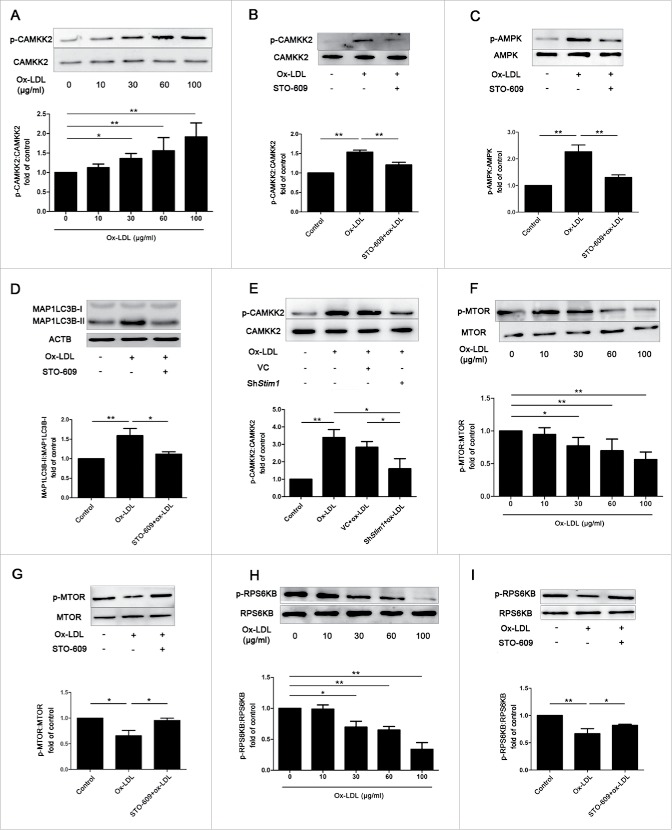
Figure 8.
Phosphorylation of CAMKK2 and dephosphorylation of MTOR are related to ox-LDL-induced autophagy. (A) EPCs were treated with different concentrations of ox-LDL (0, 10, 30, 60 or 100 μg/ml) for 12 h. Western blot analysis showed that ox-LDL dose-dependently increased phosphorylation of CAMKK2. (B and C) EPCs were pretreated with the CAMKK2 inhibitor STO-609 (10 μM) before ox-LDL (60 μg/ml) exposure, the phosphorylation of CAMKK2 and AMPK were significantly decreased compared with ox-LDL alone. (D) Western blots indicated that STO-609 reduced the ratio of MAP1LC3B-II:MAP1LC3B-I increased by ox-LDL. (E) Stim1 was silenced with shRNA for 72 h before ox-LDL (60 μg/ml) exposure 12 h, the phosphorylation of CAMKK2 was significantly decreased in Stim1-knocked down group compared with ox-LDL alone. (F) EPCs were treated with different concentrations of ox-LDL (0, 10, 30, 60 or 100 μg/ml) for 12 h. Western blots analysis showed that phosphorylation of MTOR decreased significantly at the concentration of 30, 60 or 100 μg/ml of ox-LDL. (G) STO-609 (10 μM) were pretreated with EPCs before ox-LDL (60 μg/ml) exposure, STO-609 reversed phosphorylation of MTOR compared with ox-LDL alone groups. (H) EPCs were treated with different concentrations of ox-LDL (0, 10, 30, 60 or 100 μg/ml) for 12 h. Western blots analysis showed that phosphorylation of RPS6KB decreased significantly at the concentration of 30, 60 or 100 μg/ml of ox-LDL. (I) EPCs were pretreated with STO-609 (10 μM) before ox-LDL (60 μg/ml), STO-609 reversed phosphorylation of RPS6KB compared with ox-LDL alone groups. (Cells were isolated from 3 rats for 1 experiment and 3 independent experiments were performed, western blot results were normalized to the controls (given as 1-fold), mean + SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01).