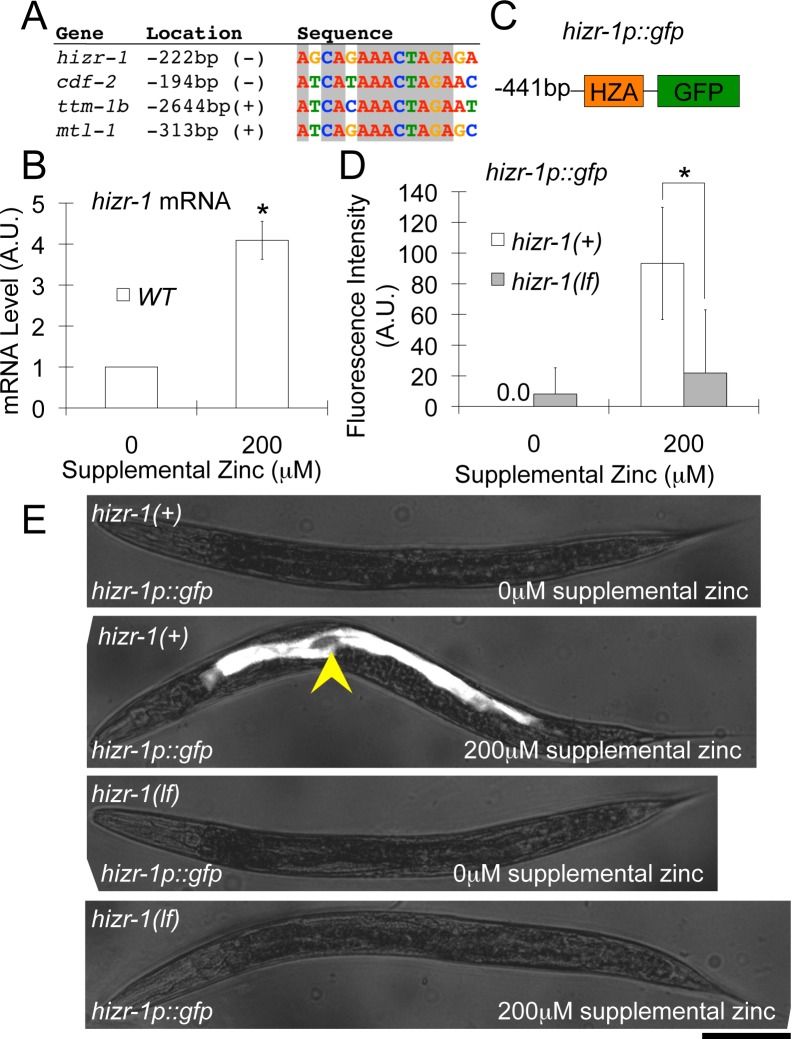
Fig 7. The hizr-1 promoter contains a HZA enhancer and is activated by high dietary zinc, which requires hizr-1 function.
(A) An alignment of the 15 bp DNA sequence of HZA elements in hizr-1, cdf-2, ttm-1b, and mtl-1; 11 positions are identical in these four sequences (boxed). The location is the first nucleotide of the DNA motif; the A residue of the translation start site (ATG) is defined as +1; (+) and (-) indicate the same and opposite orientation relative to the direction of transcription, respectively. (B) mRNA was isolated from populations of wild-type (white) animals cultured with 0 or 200 μM supplemental zinc. hizr-1 transcript levels were analyzed by qPCR; mRNA levels are expressed in arbitrary units and were normalized to rps-23, a ribosomal protein gene that is not regulated by high zinc. The values were normalized by setting the value for wild-type animals at 0 μM supplemental zinc equal to 1.0. Bars represent the average +/- S.D. (n = 3), (*, p < 0.05). hizr-1 transcript levels were increased significantly when cultured with 200 μM supplemental zinc compared to 0 μM supplemental zinc, demonstrating that it is a high-zinc–activated transcript. (C) A diagram (not to scale) of the hizr-1p::gfp transcriptional reporter construct containing the hizr-1 promoter (black line, 441 bp upstream of the ATG start codon) fused to the coding region of green fluorescent protein (green box). The hizr-1 promoter contains a HZA enhancer element (orange box). (D, E) Transgenic hizr-1(+) (white) or hizr-1(am286lf) (gray) animals expressing the hizr-1p::gfp transcriptional reporter were cultured with 0 or 200 μM supplemental zinc. (D) GFP fluorescence in the intestine was quantified by image analysis. Bars represent the average fluorescence intensity +/- S.D expressed in arbitrary units (A.U.) (n = 8–10 animals), (*, p < 0.05). In hizr-1(+) animals, GFP expression levels were increased significantly when cultured with 200 μM supplemental zinc compared to 0 μM supplemental zinc, demonstrating that the hizr-1 promoter is activated by high zinc. Compared to hizr-1(+) animals, hizr-1(am286lf) mutant animals displayed significantly lower GFP expression when cultured with 200 μM supplemental zinc, indicating a defect of high-zinc–activated transcription. (E) Images of representative transgenic animals. Intestinal fluorescence is indicated by the arrowhead and required both high dietary zinc and hizr-1 function. Scale bar is approximately 100 μm.