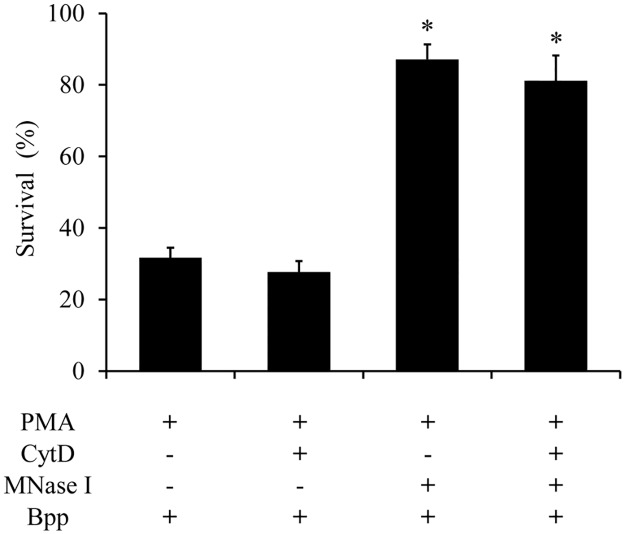
Fig 12. B. parapertussis is killed by NETs.
Neutrophils were incubated with PMA (100 nM) for 1 h at 37°C to induce NETs release. Next, neutrophils were treated with cytochalasinD (100 μg/ml; CytD), MNase I (500 mU/ml), or a combination of both for 30 min at 37°C. Neutrophils were then incubated with B. parapertussis (Bpp) (MOI 100) for 3 h at 37°C. Next, all samples were treated with MNase for 20 min to release entrapped bacteria from NETs and serial dilutions of cell lysates were rapidly plated onto bBGA to enumerate CFU. The percentage of viable bacteria was referred to bacterial inoculums. The number of viable B. parapertussis in samples treated with MNase I prior bacterial infection was significantly different from that found in samples that were not treated with MNase I. * indicates a P value <0.05 for comparison to results for PMA-treated neutrophils infected with Bpp.