Fig. 3.
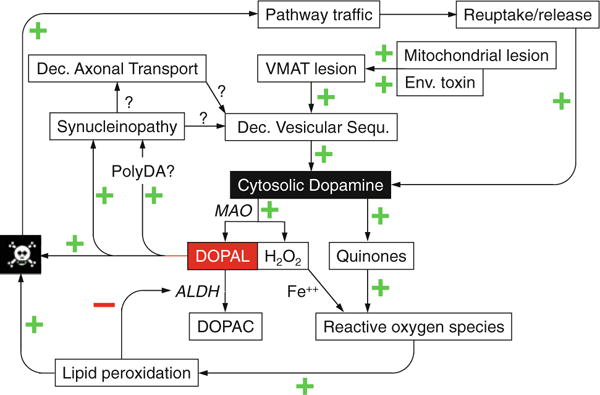
Overview of pathogenetic mechanisms in catecholaminergic neurons. Central to the vulnerability of these neurons are ongoing vesicular leakage and toxicity of cytosolic catecholamines such as dopamine, via spontaneous auto-oxidation and oxidation catalyzed by monoamine oxidase (MAO) to form dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL). DOPAL is detoxified by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) to form dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC). Other abbreviations: Dec decreased, Env environmental, PolyDA polydopamine, VMAT vesicular monoamine transporter
