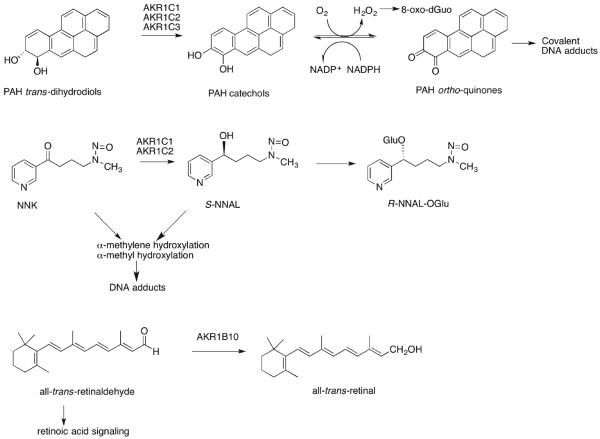
Figure 3.
Role of AKRs in human lung cancer: function of AKRs induced by the smoking gene battery. AKR1C1–3 are involved in the metabolic activation of PAH; AKR1C1 and AKR1C2 show a preference for forming S-NNAL, which can be retained in lung tissues for bioactivation, and AKR1B10 prevents retinoic acid signaling. Acting together, these reactions could contribute to lung cancer initiation and promotion.