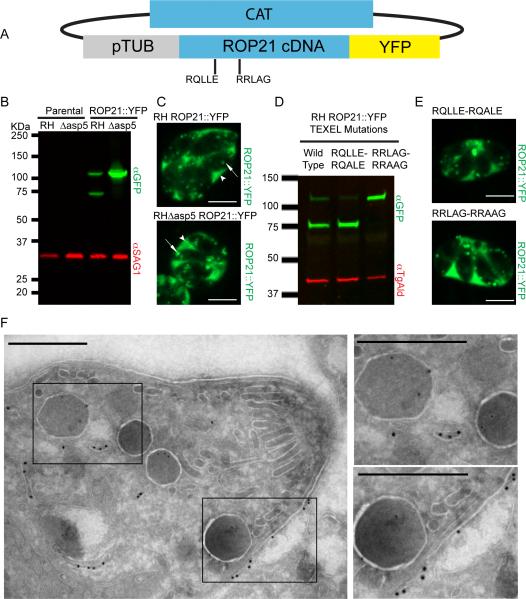
Figure 2.
Ectopic Expression and Localisation of ROP21. A. Ectopic expression of ROP21::YFP was performed by cloning ROP21 cDNA in frame with a C-terminal YFP tag, driven by the tubulin promoter; selection was provided by the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene. B. Western blot of stable clones expressing the ROP21::YFP fusion in RH wild type and RHΔasp5 background vs. parental controls. Rabbit anti-GFP was used to detect YFP and mouse anti-SAG1 was used as a loading control. C. Single frames from spinning-disc confocal video microscopy movies (Supplemental video S1 and S2) that demonstrate ROP21::YFP trafficking and secretion. Scale bar denotes 5 μm, arrow heads denote accumulation of ROP21::YFP in the PV, arrows denote intracellular vesicular/granular structures containing ROP21::YFP. D. Western blot of parasites transiently expressing ROP21::YFP and ROP21::YFP with mutated TEXEL motifs. Mouse anti-GFP was used to detect YFP and rabbit anti-TgAld was used as a loading control. E. Spinning-disc confocal microscopy images of parasites expressing ROP21::YFP containing mutated TEXEL motifs. F. Immunoelectron microscopy of RH ROP21::YFP tachyzoites. Scale bar denotes 500 nm, 18 nm gold nanoparticles mark detectable ROP21::YFP, 12 nm gold particles mark detectable GRA2. Boxed regions correspond to zoomed regions presented to right of main image.