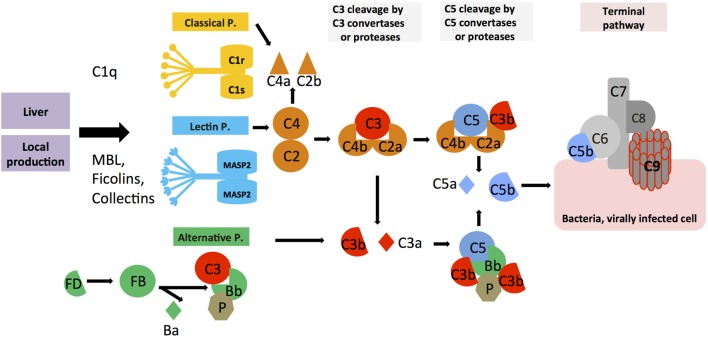
Figure 1.
Systemic complement activation. Serum-circulating complement can be activated via three pathways: the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways, which all cumulate in the formation of multiprotein complexes termed C3 convertases. The classical and lectin pathway C3 convertases (C4bC2a) and the alternative pathway C3 convertase (C3bBb) lead to cleavage of C3 into the opsonin C3b and the anaphylatoxin C3a. Properdin (P) is a stabilizator of the alternative C3 convertase. Upon subsequent generation of C5 convertase (C4bC2aC3b for the classical and lectin pathways, C3bBbC3b for the alternative pathway), C5b and the anaphylatoxin C5a are produced, with surface-bound C5b initiating the formation and insertion of the terminal complement pathway (TTC; or membrane attack complex, MAC) on pathogens (or other target membranes).