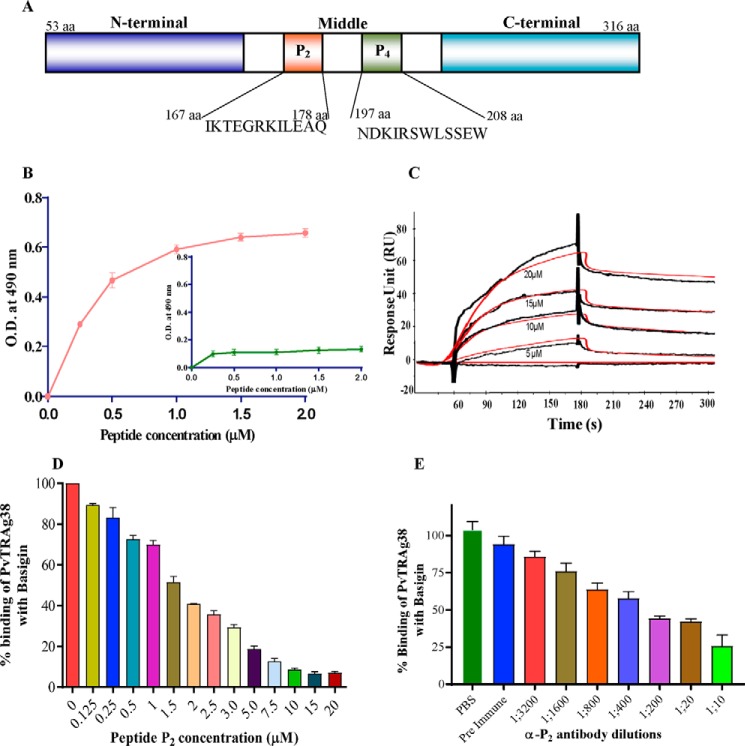
FIGURE 6.
Binding of peptide P2 of PvTRAg38 with basigin. A, schematic diagram depicting domain organization of PvTRAg38 and location of P2 and P4 regions. B, solid phase ELISA. Increasing concentrations (0–2 μm) of recombinant histidine-tagged basigin was added to the wells of an ELISA plate already coated with 1 μm peptide P2 or peptide P4 (inset). The plate was developed with anti-His6 monoclonal antibody as described in text. Mean ± S.D. value of absorbance from three experiments is plotted. C, SPR analysis of basigin interaction with P2 peptide. Recombinant basigin was immobilized on the cell of CM5 chip by the amine coupling method. Four different concentrations of P2 peptide (5–20 μm) were injected at a flow rate of 30 μl/min over the surface of immobilized basigin. Curve fit (Langmuir 1:1 model) sensograms show dose-dependent response of P2 peptide binding with basigin. D, specificity of peptide P2 binding to basigin by competition assay. Increasing concentrations of peptide P2 (0–20 μm) were incubated for 2 h with untagged recombinant basigin immobilized on an ELISA plate well. After washing, a fixed concentration of GST-tagged PvTRAg38 was added to the wells, and bound protein was detected with GST monoclonal antibody as described in the text. Binding in the absence of peptide P2 was taken as percentage control for the rest of the concentrations. The mean value of three independent experiments is plotted with S.D. E, specificity of peptide P2 binding with basigin by antibody inhibition assay. Different dilutions of anti-P2 rabbit antibodies were incubated for 2 h with GST-tagged PvTRAg38 immobilized on an ELISA plate well. After washing, a fixed concentration of histidine-tagged basigin was added to the wells. The bound histidine-tagged basigin was detected by the anti-His6 monoclonal antibodies, as described in the text. The mean value of three independent experiments is plotted with S.D.