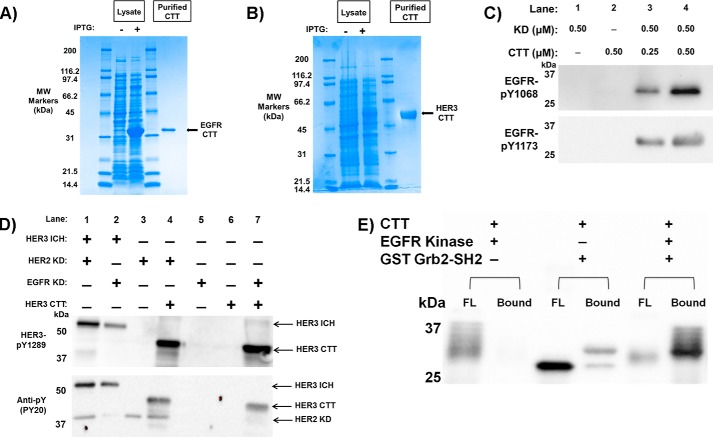
FIGURE 4.
Purification and phosphorylation of CTT constructs. A, Coomassie-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel of EGFR CTT purification. Lanes 1 and 4 are molecular weight markers labeled respectively. Lane 2 is transformed cell lysate preinduction with IPTG. Lane 3 is lysate postinduction. Lane 5 is purified EGFR CTT following Ni2+-chelating chromatography and gel filtration. EGFR CTT purity was determined to be >95%. B, Coomassie-stained SDS-polyacrylamide gel of HER3 CTT purification. This gel uses similar lane arrangement as in A for HER3 CTT expression. C, EGFR CTT is recognized and phosphorylated by the EGFR kinase domain. Phosphospecific antibodies to EGFR Tyr(P)-1068 and EGFR Tyr(P)-1173 were used to detect CTT phosphorylation. D, Western blotting analysis of HER3 CTT phosphorylation. The HER3 ICH serves as a positive control showing C-terminal tail phosphorylation via interaction with EGFR KD or HER2 KD. HER3 CTT is recognized and phosphorylated by the EGFR and HER2 kinase domains just as it would be as if it was part of its ICH construct. Phosphospecific antibodies to HER3 Tyr(P)-1289 and general anti-phosphotyrosine PY20 were used to detect HER3 CTT phosphorylation. E, phosphorylated EGFR CTT binds to the Grb2 SH2 domain. GSH-agarose beads were preloaded with GST-tagged Grb2 SH2 domain protein. Phosphorylated or unphosphorylated EGFR CTT was then incubated with the beads for 2 h at 4 °C, flow-through (FL) was collected and washed, and then the beads were boiled in sample buffer (Bound). Fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE and then transferred to nitrocellulose. Anti-His6-HRP antibody was used to detect EGFR CTT in the FL and bound fractions.