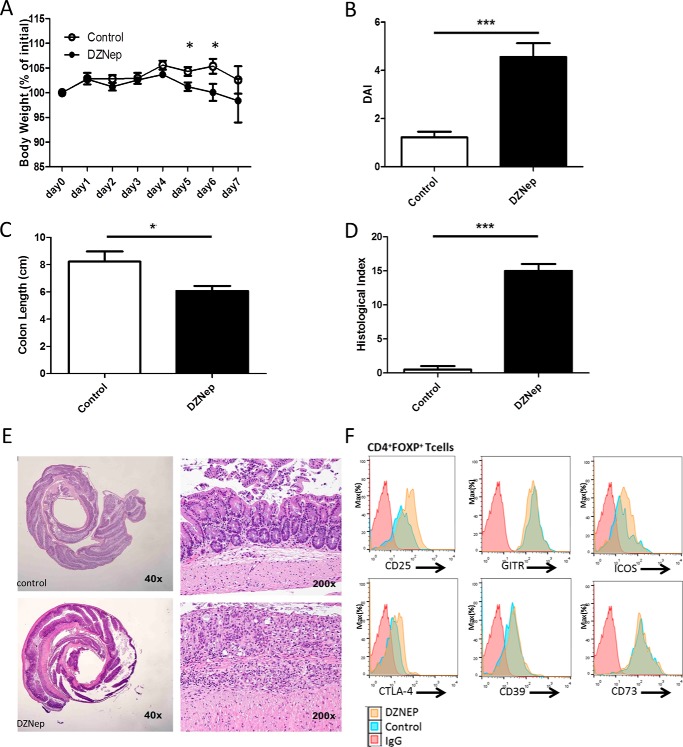
FIGURE 5.
Pharmacologic inhibition of EZH2 results in heightened intestinal immune reactivity. A–D, demonstration of weight change (A), clinical disease activity index (DAI, B), colon length (C), and blinded histologic inflammatory index (D) in DZNep-treated animals versus sham-treated controls exposed to 2% DSS. E, representative colon histologic section demonstrating significant inflammation and ulceration. Statistical significance for weight change was determined using the Holm-Sidak method, with α = 5.000% (p < 0.05). Each time point was analyzed individually without assuming a consistent S.D. For colon length and histologic and disease activity index, significance was determined using a non-parametric unpaired t test of significance (Mann-Whitney), p < 0.05. The data are generated from n = 20 animals, 10/group. F, expression of cell surface markers in Treg cells (CD4+FOXP3+) measured by flow cytometry. Data are representative of n = 4 mice/experimental group. *, p ≤ 0.05; ***, p ≤ 0.0001.