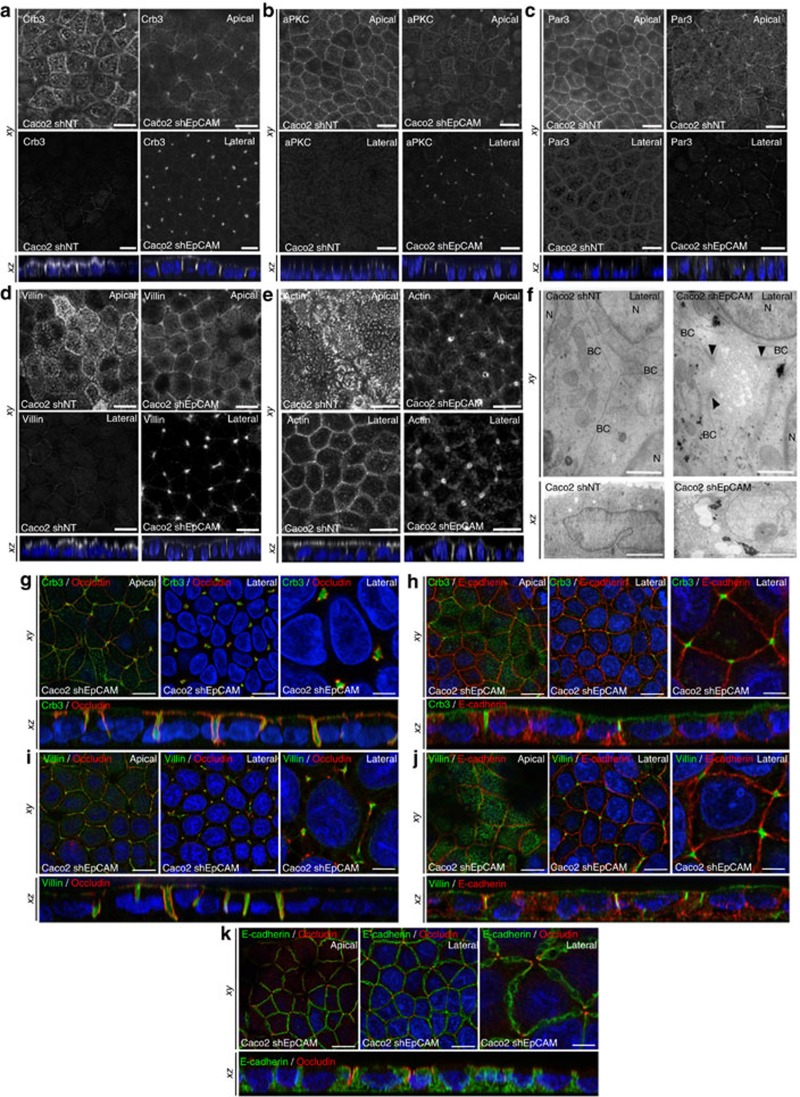
Figure 3. Apical domain is unusually displaced at tricellular junctions through EpCAM silencing.
(a–e) Confocal microscopy analysis of Crb3 (a), aPKC (b), Par3 (c), villin (d) and actin (e) on the apical or lateral sides in control (Caco2 shNT, left panels) and EpCAM-depleted (Caco2 shEpCAM, right panels) cells. xy and xz views are presented showing the relocated apical markers at tricellular junctions. Scale bars, 5 μm. (f) TEM ultrastructural analysis of tricellular contacts in control (Caco2 shNT, left) and EpCAM-depleted (Caco2 shEpCAM, right) cells, showing microvilli at tricellular contacts. Arrowheads point to TJs. Longitudinal (xy) and transversal views (xz) are presented. BC, bicellular contact, N, nucleus. Scale bars xy, 1 μm and xz, 2 μm. (g–k) Confocal microscopy analysis of double immunostainings for Crb3 (green) and occluding (red) (g), Crb3 (green) and E-cadherin (red) (h), villin (green) and occluding (red) (i), villin (green) and E-cadherin (red) (j), and E-cadherin (green) and occluding (red) (k) on the apical or lateral sides in EpCAM-depleted (Caco2 shEpCAM) cells. xy and xz views are presented. Scale bars, 5 μm; high magnifications, 2 μm. Nuclei were detected with Hoechst 33342 staining (blue).