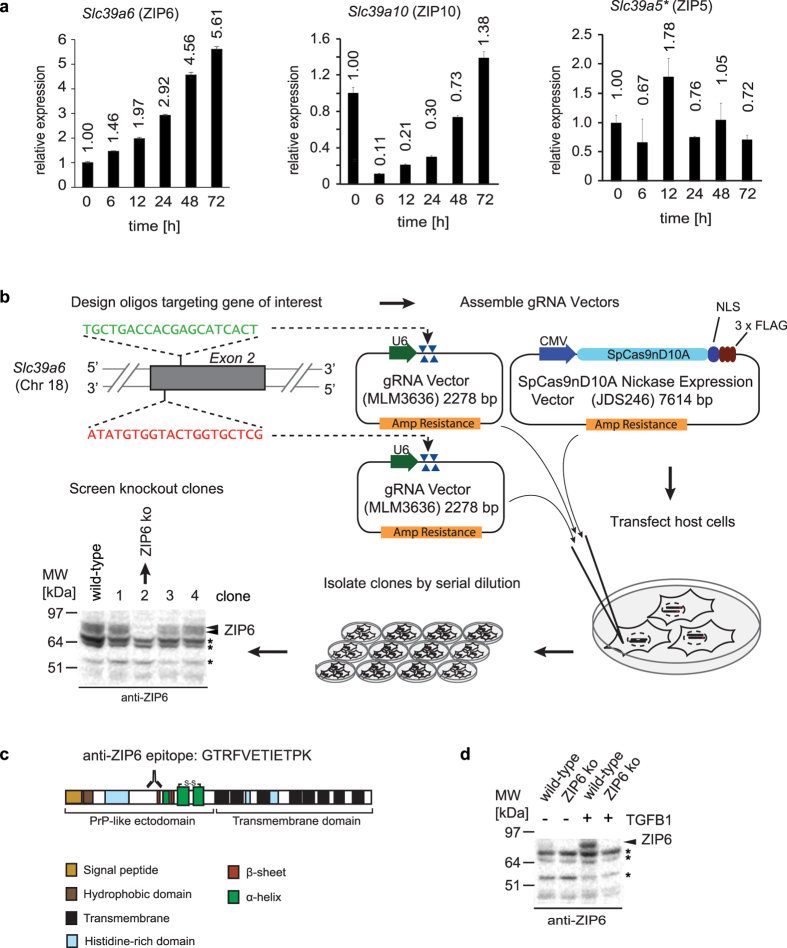
Figure 1. Mouse NMuMG cell model and tools for investigating role of ZIP6 during EMT.
(a) ZIP6 transcript levels are more than five-fold increased during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induced in NMuMG mouse epithelial cells upon 72 h exposure to TGFB1. The asterisk in this panel designates the fact that this quantitation had to be based on relatively low levels of ZIP5 mRNAs in NMuMG cells, making this quantitation less robust than those depicted for ZIP6 and ZIP10. (b) Strategy employed for CRISPR-Cas9-based knockout of ZIP6 protein expression in NMuMG cells following Cas9-D10A nickase-mediated single-strand cleavages of Slc39a6 Exon 2 at non-overlapping target sites. (c) Schematic of ZIP6, indicating peptide epitope of in-house generated polyclonal antibody used in this work. (d) Evidence of ZIP6 protein level increase in NMuMG cells upon 48 h exposure to TGFB1. Bands labeled with asterisks indicate non-specific bands.