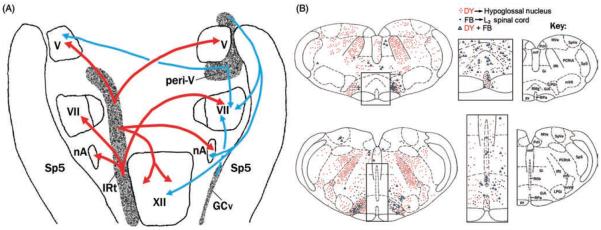
Figure 3.
Major sources of pontomedullary afferent projections to the orofacial motor nuclei. (A) Schematic dorsal view of the most prominent afferent pathways common to all orofacial motor nuclei. The medullary IRt is the main source of bilateral projections to the trigeminal (V), facial (VII), hypoglossal (XII), and ambiguus (nA) motor nuclei (red arrows). The projections to these motor nuclei tend to exhibit a distinct rostrocaudal pattern. The projections to orofacial motor nuclei that originate in the pontine reticular region surrounding the trigeminal motor nucleus (peri-V), and the ventrolateral medullary gigantocellular region (GCv) tend to be unilateral (blue arrows). (Fig. 12 from Ref. 551 colorized and republished with permission from John Wiley and Sons obtained via the Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.) (B) Major medullary sources of afferent projections to the XII nucleus in relation to the descending spinal collaterals of selected XII premotor neurons, as revealed by large retrograde tracer injections into the XII motor nucleus and ventral horns of the lumbar (L2) spinal cord. The two medullary levels illustrated are located rostral to the XII nucleus. Consistent with data in A, the IRt region contains the largest number of neurons retrogradely labeled with Diamidino Yellow (DY) tracer from the XII nucleus (red dots). Notably, no cells retrogradely labeled with Fast Blue (FB) tracer from the spinal cord (black dots) are located in this region. Additional medullary XII premotor neurons are located along the midline (enlarged images in the middle), the gigantocellular region pars α (GiA), and the lateral paragigantocellular (LPGi) region. A small fraction of cells in these medial and ventral locations has divergent projections to the XII nucleus and lumbar spinal cord (blue triangles). The key to anatomical regions is shown on the right. (Modified from Fig. 3B in Ref. 323 and republished with permission from John Wiley and Sons obtained via the Copyright Clearance Center, Inc.) Additional abbreviations in A and B: Gi, gigantocellular reticular region; mlf, medial longitudinal fasiculus; MVe, medial vestibular nucleus; PCRtA, parvicellular reticular area; PrH, nucleus prepositus hypoglossi; py, pyramidal tract; RMg, Rob, Rpa, raphé magnus, pallidus, and obscurus nuclei; Sp5, spinal trigeminal sensory nucleus; SpVe, spinal vestibular nucleus.