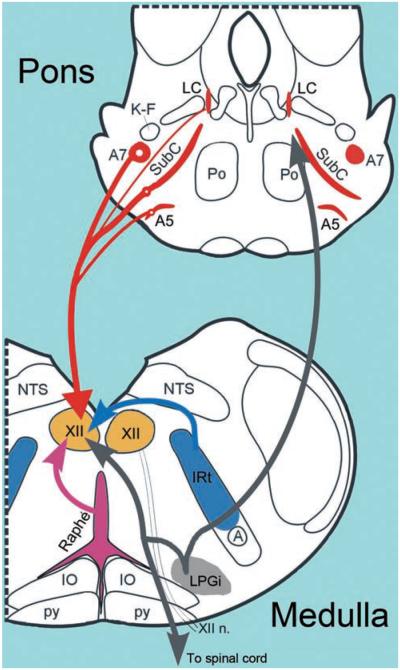
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the four key neuroanatomically and neurochemically distinct inputs to the XII nucleus. NE afferents originate mainly in the pontine A7 and A5 groups and the SubC region, whereas the largest group of NE neurons, the LC, has negligible projections to the XII nucleus. For clarity, NE projections are shown on one side only; they are bilateral with a minor ipsilateral predominance. 5-HT afferents come from the medullary raphé pallidus and obscurus nuclei, as well as the lateral wings of the medullary raphé. The medullary IRt contains glutamatergic and cholinergic XII premotor cells; the former provide inspiratory drive to XII motoneurons, and the latter may mediate pre- or postsynaptic modulatory influences that are either respiratory or state dependent. The LPGi and the adjacent areas contain cells that have been hypothesized to mediate active inhibitory effects of REM sleep to motoneurons. GABAergic, REM sleep-active neurons with divergent projections ascending to the pons and descending to the spinal cord have been located in this area (579). It is not known whether the same cells also have axonal projections to the XII nucleus. Abbreviations: A, nucleus ambiguus; IO, inferior olive, Po, nucleus pontis oralis; K-F, Kölliker-Fuse nucleus; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; py, pyramidal tract.