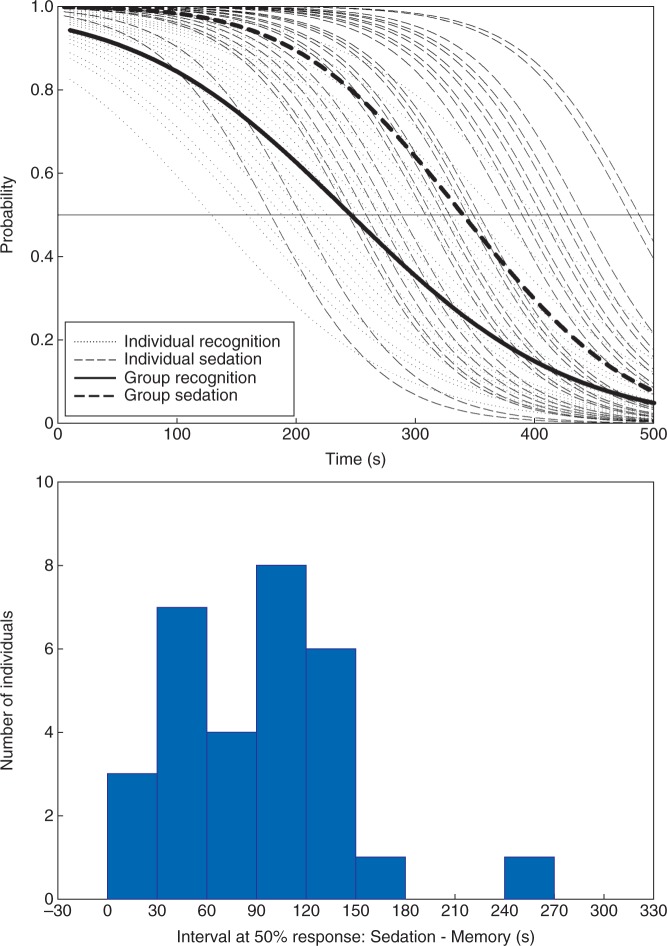
Fig 1.
Individual probabilities (faint plots) of verbal responses (sedation) and subsequent recognition memory with time (s) as the predictor variable during the induction of dexmedetomidine sedation. Group average plots are indicated in bold. Probability of recognition memory consistently decayed before onset of sedation, and the distribution of time intervals between 50% probabilities are shown in part (B). Positive values indicate that 50% recognition memory occurred sooner than 50% sedation.