Figure 1.
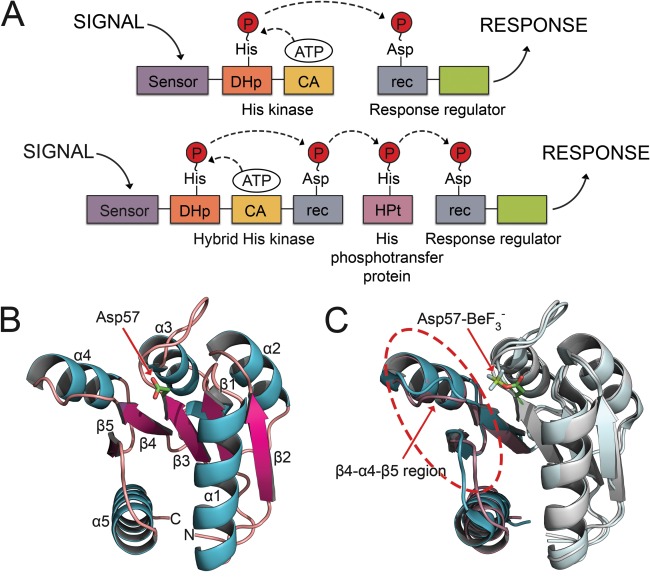
Domain arrangements for TCS systems and topology and induced conformational changes of rec domains. A: Canonical TCS pathway (top) and expanded multistep phosphorelay (bottom). In a typical TCS pathway, the signal is sensed by an HK, which binds ATP in a catalytic domain and autophosphorylates a histidine residue within the DHp. The phosphoryl group is transferred to an aspartate on the receiver domain (rec) of a downstream RR protein. Phosphorylation of the rec domain elicits a cellular response. Expanded phosphorelay systems contain an hybrid HK, with its own receiver domain, and an intermediate known as a HPt. B: The crystal structure of the representative RR, CheY (PDB 3CHY), in its unphosphorylated state shows the common (βα)5 topology. C: Major conformational shifts upon phosphorylation occur within the β4‐α4‐β5 regions (circled). Unphosphorylated CheY (PDB 3CHY) in cyan. bound CheY (PDB 1FQW) in purple. Asp57‐ is shown in stick model.
