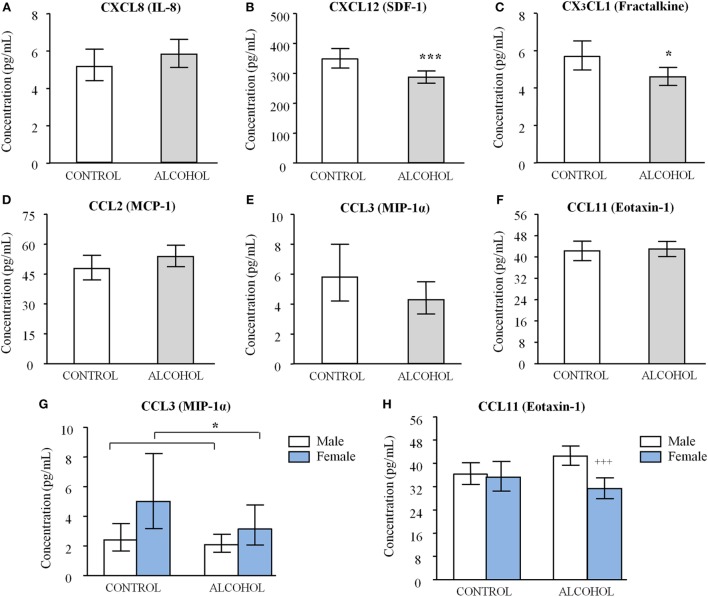
Figure 1.
Plasma chemokine concentrations in abstinent alcohol use disorders (AUD) patients and control subjects. (A) CXCL8 [interleukin-8 (IL-8)]; (B) CXCL12 [stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)]; (C) CX3CL1 (fractalkine); (D) CCL2 [monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)]; (E) CCL3 [macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha (MIP-1α)]; and (F) CCL11 (eotaxin-1) concentrations according to “history of AUD.” Bars are estimated marginal means and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) (picograms per milliliter). Data were analyzed by two-way analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) and *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 denote a significant main effect of “history of AUD.” (G) CCL3 (MIP-1α) and (H) CCL11 (eotaxin-1) concentrations according to “history of AUD” and “sex.” Bars are marginal means and 95% CI (picograms per milliliter). Data were analyzed by two-way ANCOVA and *p < 0.05 denotes a significant main effect of “sex.” +++p < 0.001 denotes significant differences compared to male AUD patients because there was an interaction of factors.