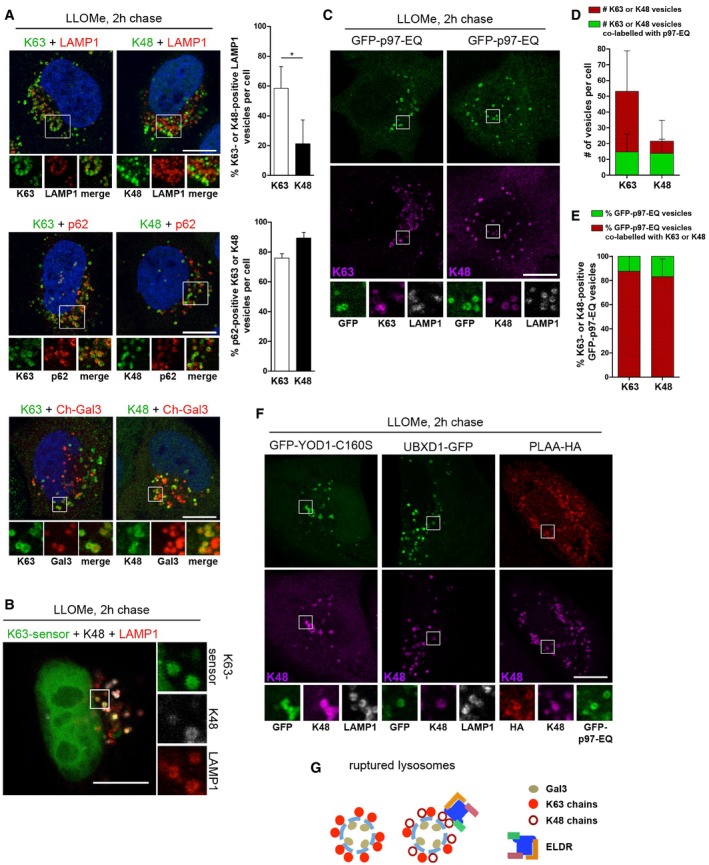
K63 and K48 ubiquitination of damaged lysosomes. Untransfected HeLa cells, or cells expressing mCherry‐Gal3 (Ch‐Gal3) were LLOMe‐treated for 1 h. Two hours after washout, cells were stained with antibodies specific for K63 or K48 chains, and LAMP1 or p62 as indicated. Percentage of K63‐ or K48‐ubiquitinated LAMP1 vesicles and percentage of p62‐positive K63 or K48 vesicles were quantified from three independent experiments (mean ± SD, Student's unpaired t‐test for LAMP1). *P < 0.05.
Colocalization of K63‐ and K48‐linked ubiquitin conjugates on individual lysosomes. Cells expressing GFP‐TAB2‐NZF (K63‐sensor) were treated as in (A) and stained for K48 chains and LAMP1. Note that the apparent nuclear localization of the sensor is a consequence of the extraction procedure (van Wijk
et al,
2012).
Cells expressing GFP‐p97‐EQ were treated as in (A) and stained with antibodies as indicated.
Quantification of the total number of K63‐ or K48‐ubiquitinated vesicles per cell, and number of p97‐EQ positive K63‐ or K48‐ubiquitinated vesicles (mean ± SD).
Percentage of GFP‐p97‐EQ vesicles positive for K63 or K48 chains was determined (mean ± SD).
ELDR components target K48 conjugates on lysosomes. Detection of GFP‐YOD1‐CS or UBXD1‐GFP alone, or co‐transfected with PLAA‐HA and GFP‐p97‐EQ, 2 h after LLOMe washout and co‐stained with indicated antibodies.
Scheme of ubiquitination of lysosomes after damage. K48‐linked ubiquitination occurs on a subpopulation of lysosomes decorated with K63‐linked chains. The ELDR components specifically target K48‐linked ubiquitin conjugates.
Data information: Scale bars, 10 μm.