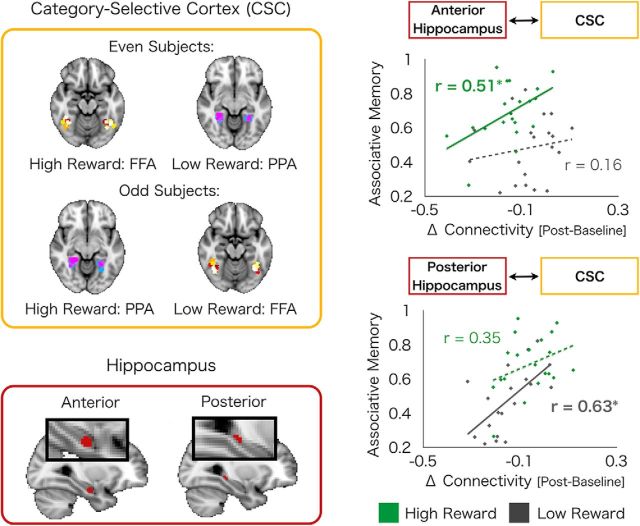
Figure 3.
Postencoding interactions between the hippocampus and CSC predict 24 h associative memory. Experience-dependent changes in coupling (postencoding > baseline) of CSC (top left) with anterior and posterior hippocampus (bottom left) differentially predict high- and low-reward memory. Interactions between anterior hippocampus with high-reward CSC predict high-reward memory, although no such relationship exists between anterior hippocampus-low-reward CSC interactions and low-reward memory (top right). Conversely, interactions between posterior hippocampus with low-reward CSC predict low-reward memory, although no such relationship exists between posterior hippocampus-high-reward CSC interactions and high-reward memory (bottom right). High- and low-reward CSC refers to CSC associated with high- and low-rewards during encoding, respectively. Green dots indicate high-reward values. Gray dots indicates low-reward values. Solid lines indicate significant correlations. *p < 0.05. Hyphenated lines indicate nonsignificant correlations.