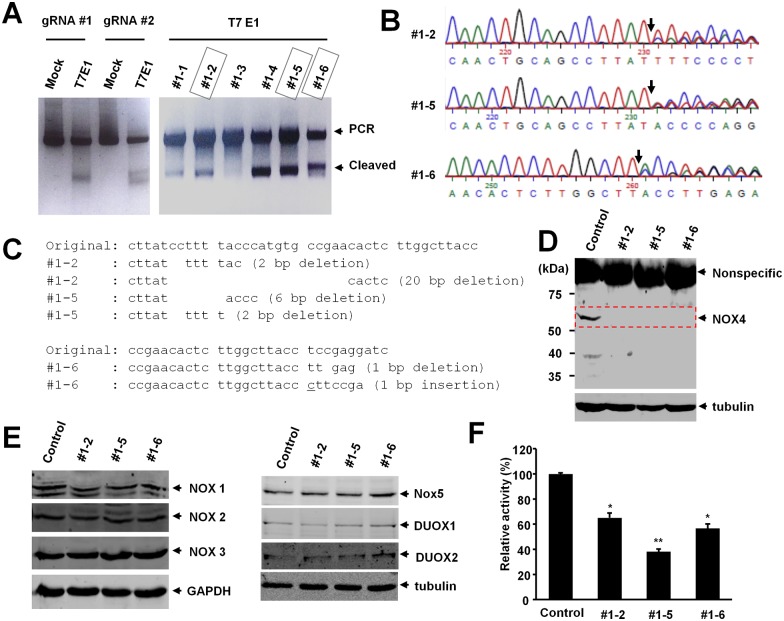
Fig 1. Generation and validation of NOX4 knockout (KO) HeLa cell lines.
(A) T7 endonuclease 1(T7E1) assay. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with either pX459/NOX4 gRNA #1 or pX459/NOX4 gRNA #2, and genomic PCR products were analyzed by T7E1 assay (left panel). HeLa cells transfected with pX459/NOX4 gRNA’s were selected with puromycin and single colonies were isolated. The genomic PCR product of each clone was analyzed by T7E1 assay (right panel). Experiments were repeated three times with similar observations, and representative images are shown. (B) DNA sequence analysis showed the presence of the NOX4 mutation in clones #1–2, #1–5 and #1–6. The black arrows indicate the heterogeneous genomic DNA sequences in each cell lines. (C) CRISPR-Cas9 introduced the insertion and deletion (indel) mutation in the target sites. (D) Western blot of NOX4 knockout cell lines. Equal amount of HeLa control and NOX4 knockout cell lysates were probed with anti-NOX4 antibody. Experiments were repeated three times with similar observations, and representative data is shown. (E) NOX4 knockout did not influence NOX1, NOX2, NOX3, NOX5, DUOX1 and DUOX2 levels. Protein levels of NOX1, NOX2, NOX3, NOX5, DUOX1 and DUOX2 in parental HeLa cells and three clones of NOX4 knockout cells. (F) NOX4 knockout showed lower H2O2 production. The levels of H2O2 were measured with the Amplex Red assay in triplicate. The graph shows the average and the standard deviation (SD). Control vs knockout cells. *: P <0.005, **: P <0.0001.