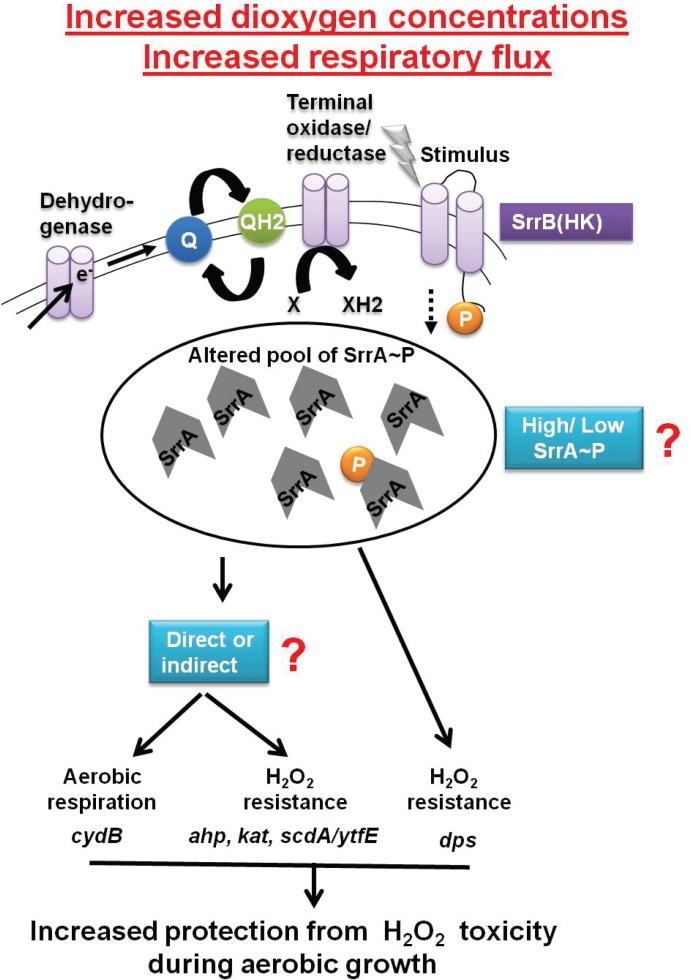
Fig 9. Working model for the role of SrrAB in modulating the transcription of genes utilized in H2O2 resistance and dioxygen respiration.
SrrAB modulates gene transcription in response to cellular respiratory flux [36]. We propose that increased culture aeration leads to increased respiratory flux during post-exponential growth, which results in altered kinase activity of SrrB and variation in the cellular pool of SrrA~P. An altered SrrA~P pool results in increased expression of genes under the SrrAB regulon that are utilized for H2O2 resistance and dioxygen respiration. The resultant physiological changes allow for cellular homeostasis by protecting macromolecules against H2O2 toxicity that arise during dioxygen respiration.