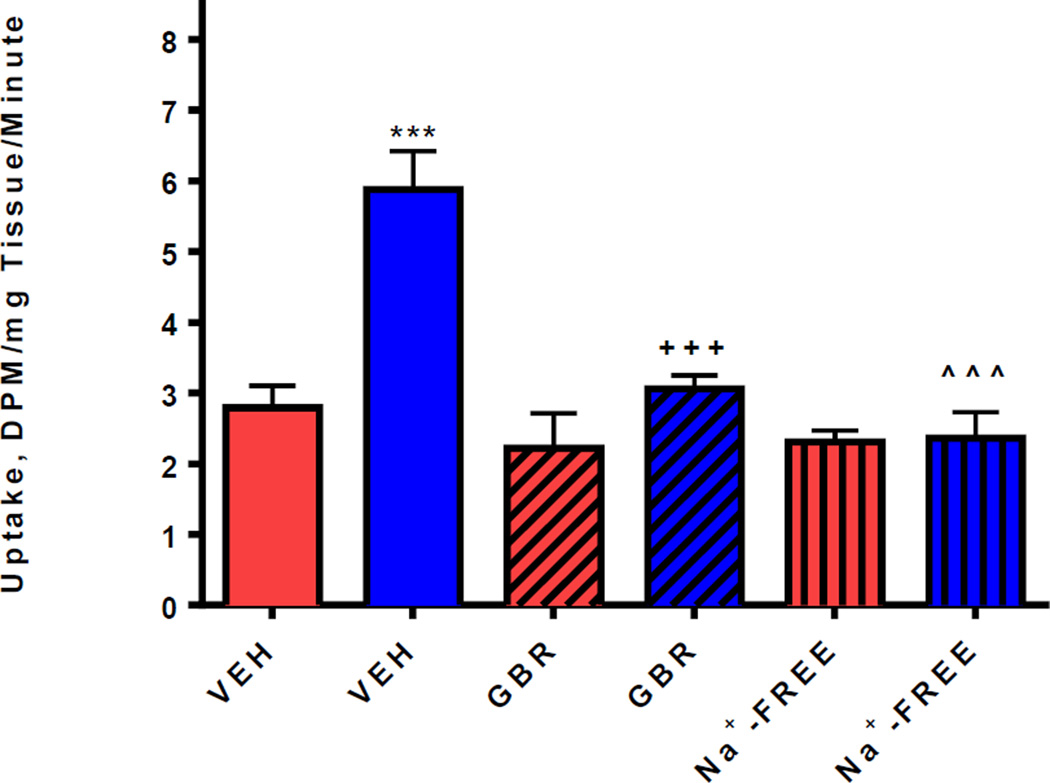
Figure 2. Uptake of [3H]Dopamine into hairy root cultures of L. cardinalis.
The first two bars compare [3H]Dopamine uptake into wildtype hairy roots (blue bars) with that into transgenic hairy roots (red bars). Cultures were incubated with [3H]Dopamine for 30min at 37°C, non-specific uptake was determined at 0°C. For each replicate, the radioactivity taken up by 10 roots was pooled and specific uptake calculated by subtracting non-specific uptake from total uptake values. Each bar represents four averaged replicates and data is expressed as mean±SEM DPM/mg tissue. The transgenic hDAT hairy roots showed significantly greater uptake of [3H]Dopamine (5.88±0.54^^^, One-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc, P<0.001) than wildtype (2.79±0.31). Pretreatment with the selective inhibitor of the DAT, GBR12909 (100µM,+++, One-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc, P<0.001), prevented the increased uptake of [3H]Dopamine into transgenic hDAT hairy roots, as did substitution of Na+-containing buffer with Na+-free buffer (***, One-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc, P<0.001) (the function of the hDAT requires the presence of Na+), relative to vehicle-treated controls expressing hDAT(blue bar, VEH).