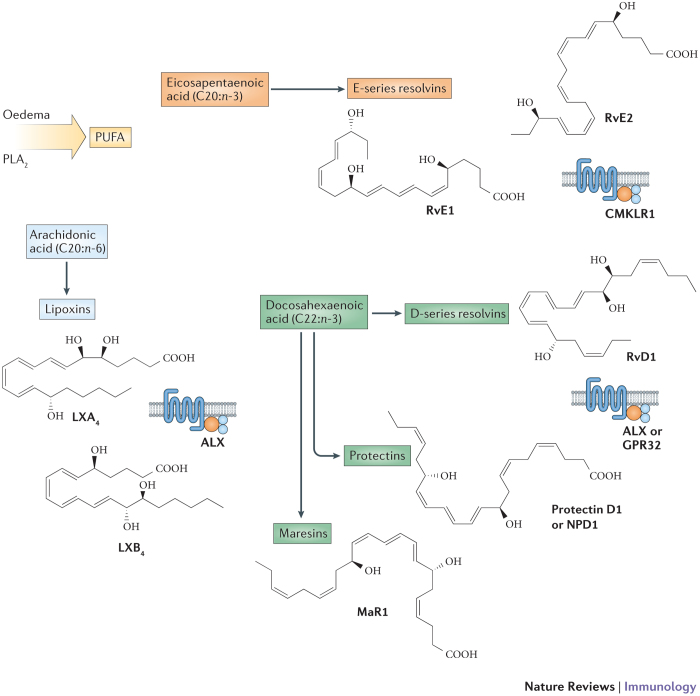
Figure 2. Polyunsaturated fatty acids are substrates for specialized pro-resolving mediators.
Stereoselective mediators that enhance host defence, resolve tissue inflammation and stimulate tissue regeneration have been described4. These specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) are produced in a spatio-temporally regulated manner from essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are either released enzymatically by phospholipase A2 (PLA2) from cell membranes for secondary conversion by biosynthetic enzymes or delivered with oedema fluid from plasma to exudates. The principal SPM families are lipoxins from arachidonic acid (C20:4n-6; in light blue), as well as the E-series resolvins from eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5n-3; in pink) and D-series resolvins, protectins and maresins from docosahexaenoic acid (C22:6n-3; in green). The SPM precursors eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid are essential omega-3 PUFAs. Representative members of these families, their structures and receptors are shown here. CMKLR1, chemokine-like receptor 1; GPR32, probable G protein-coupled receptor 32; LX, lipoxin; MaR1, maresin 1; NPD1, neuroprotectin D1; RvD1, resolvin D1; RvE, resolvin E.