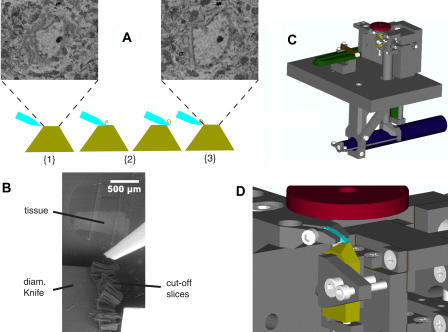
Figure 2. SEM Microtomy.
(A) Principle of SBFSEM operation: (1) a SEM image is taken of the surface of the plastic-embedded tissue preparation (amber trapezoid). (2) Then with a diamond knife (blue) an ultrathin slice is cut off the top of the block. (3) After retraction of the knife, the next picture is taken. The pictures shown are from an actual stack (cerebellar cortex) but are not successive slices; rather, they are spaced by five images (about 315 nm) to make the changes more apparent.
(B) Usually cut-off slices pile up on the top of the knife. Protruding into the picture from the right is a puffer pipette, occasionally used to remove debris from the knife.
(C and D) The mechanical design for the in-chamber microtome is shown in an overview (C) and a close-up of knife and sample (D) in renderings from the computer-aided design software. Most parts are nonmagnetic stainless steel (grey). A large-motion leveraged piezo actuator (green part on the left) drives the knife holder back and forth. The custom diamond knife (light blue) is clamped in a special holder. The sample (amber) advance is driven via a lever by a direct-current-motor-driven micrometer (dark blue). The retraction during the backwards knife motion is again piezo actuated (green cylinder in the lower right of [C]). Bearing springs are brown. The BSE detector (red) is depicted schematically above the sample. Not shown is the lateral positioning mechanism.