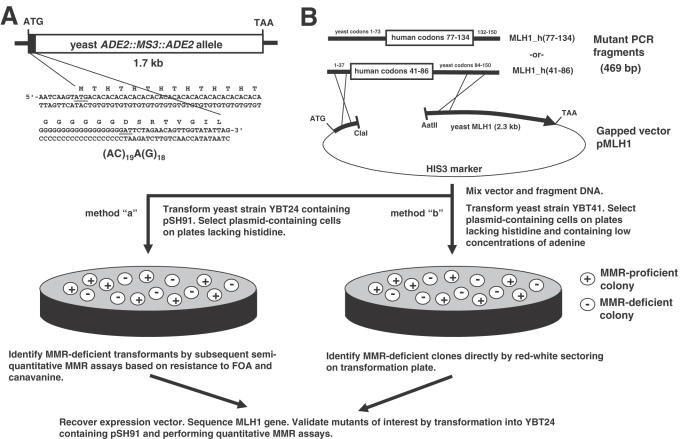
Figure 1.
(A) Sequence of the 5′ end of the ADE2::MS3::ADE2 reporter allele. The microsatellite (AC)19A(G)18 was inserted between the ATG initiator codon and the second codon (GAT) of the native ADE2 gene. The ADE2::MS3::ADE2 allele was introduced into haploid yeast strain YBT24 (mlh1Δ), replacing the native ADE2 allele to generate strain YBT41. (B) Schematic representation of the screen for inactivating mutations in MLH1. Fragments of human-yeast hybrid genes pMLH1_h(41-86) and pMLH1_h(77-134) were generated by error-prone PCR, mixed with a ClaI–AatII-digested pMLH1 expression vector and transformed into strains YBT24 (Method ‘a’) or YBT41 (Method ‘b’). Circularized plasmids were formed in vivo by homologous recombination between the PCR product and gapped vector. Yeast transformants with a MMR-deficient phenotype (i.e. containing a mutant mlh1 gene) are identified phenotypically as described in the figure. Plasmids containing the mutant mlh1 gene are recovered by shuttling into E.coli and sequenced to determine the nucleotide alteration(s) present in the mutagenized gene.