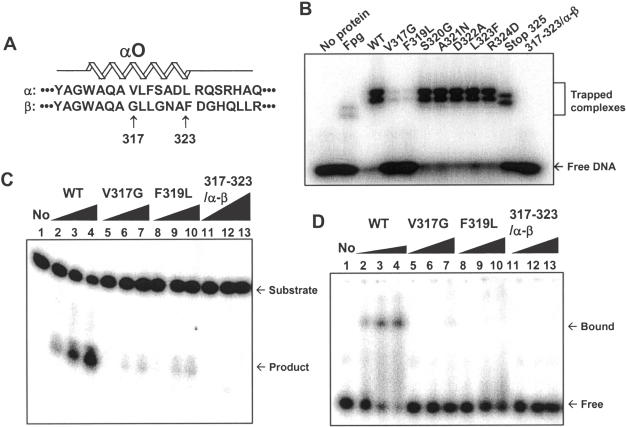
Figure 7.
Screening of 8-oxoG DNA glycosylase-deficient mutant α-Ogg1 proteins. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the αO helix domain from α- and β-Ogg1 proteins. αO helix domain is located between amino acids 313–323 in α-Ogg1. Since the first 316 amino acids are common between α- and β-Ogg1 proteins, only positions 317–323 were targeted for site-directed mutagenesis. Each amino acid in α-Ogg1 was substituted with the corresponding amino acid in β-Ogg1. As a result, V317G, F319L, S320G, A321N, D322A, L323F His–α-Ogg1 mutant proteins were generated. R324D was also generated to test the effect of αO helix-end capping. In addition, all seven amino acids in α-Ogg1 were substituted at once for those in β-Ogg1 (317–323/α-β). To exclude the effect of positions 326–345 in α-Ogg1 on the activity, a Stop325 protein was also generated, in which positions 326–345 were deleted. (B) DNA trapping assay: 1 pmol of each protein was applied to a NaBH4-mediated DNA trapping assay with oligonucleotide containing 8-oxoG/C, as described earlier. Purified Fpg protein (30.2 kDa) was used as positive control. (C) DNA incision assay with mutant proteins. WT, V317G, F319L and 317–323/α-β Ogg1 proteins were used for DNA incision assay with 10 nM of oligonucleotides containing 8-oxoG/C. The protein amounts added were 0 (lane 1), 1 nM (lanes 2, 5 and 8), 5 nM (lanes 3, 6 and 9) and 10 nM (lanes 4, 7 and 10). For lanes 11–13, 10 nM (lane 11), 100 nM (lane 12) and 500 nM (lane 13) of 317–323/α-β α-Ogg1 mutant proteins were added to reactions. (D) DNA binding assay: 10 nM of oligonucleotide containing 8-oxoG/C was incubated with WT (10, 50 and 100 nM), V317G, F319L and 317–323/α-β (10, 100 and 500 nM). Products were analyzed by EMSA.