Figure 6. Forward genetic screens isolated two mutants with strong defects in MMB chemotaxis.
(A) Response of the two mutant lines to MMB, IAA, and Benzaldehyde (BA; n = 4–8 trials for each odorant tested). The mutants showed strong defects in MMB chemotaxis but remained attracted to two other odorants, IAA and BA. (B) SNP mapping with the Hawaiian polymorphic strain CB4856 revealed that the mutations in both mutants were located on chromosome X. Mutants #7–22 and #18–10 were crossed to CB4856 and three F2 progeny from each mutant line that had MMB chemotaxis defects were analyzed for eight SNP markers on each chromosome. (C) Mutants #7–22 and #18–10 failed to complement. Responses of the F1 progeny from a cross between the two mutants to 10−4 dilution of MMB. (Mean ± SD, n = 5–8 trials).
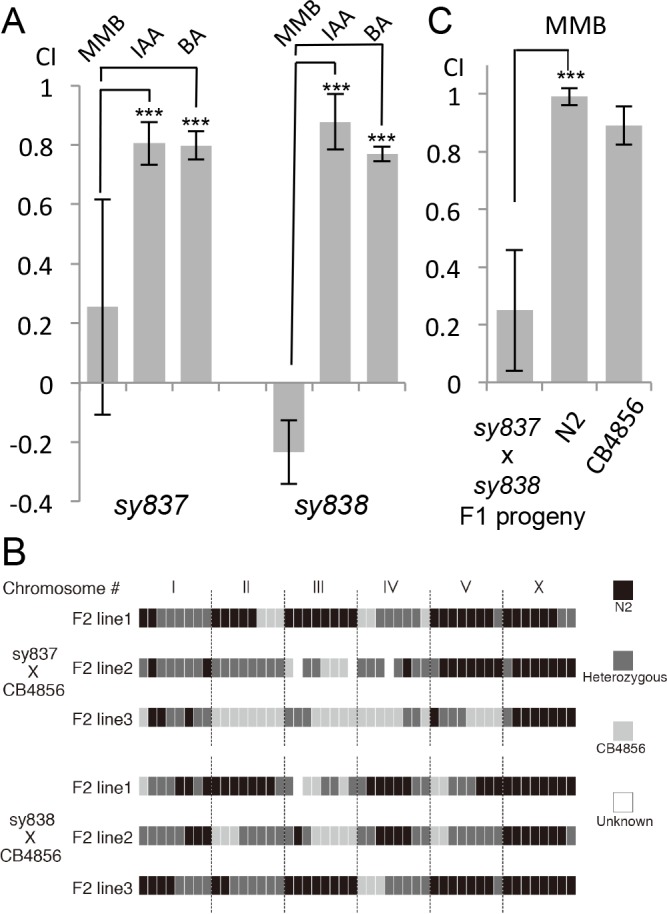
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Gene structure of odr-7.
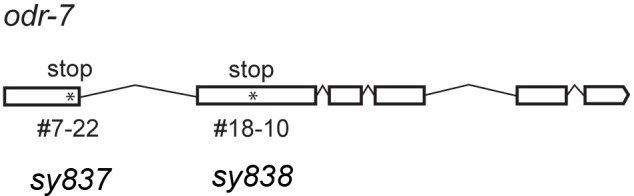
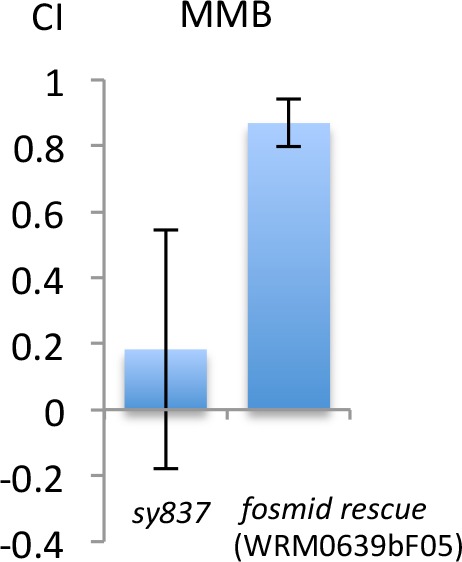
Figure 6—figure supplement 2. Fosmid clone WRM0639bF05 which contains odr-7 rescues the MMB attraction defect of odr-7 (sy837).