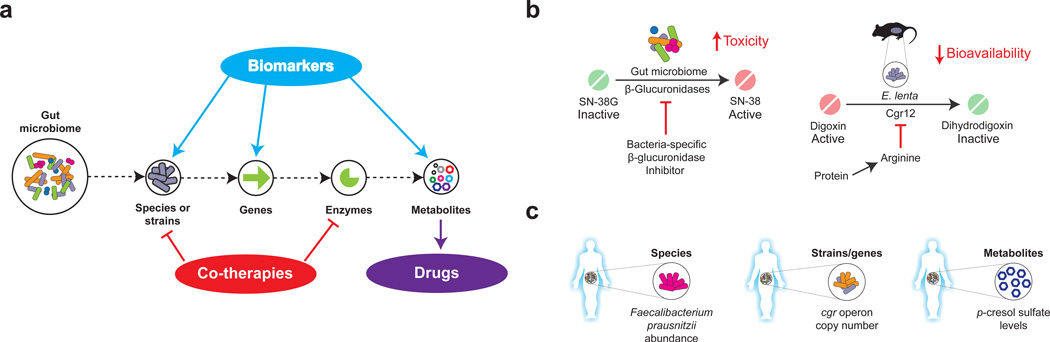
Figure 5. Translational implications of microbiome research in pharmacology.
A. Metagenomic and metabolomic approaches enable the dissection of microbial communities at multiple scales from complex communities to individual metabolites. This information can be used to find biomarkers, to develop co-therapies that target the microbiota or to identify novel drugs. B. Inhibiting microbial enzymes in the gut. Such examples include using small molecules to inhibit bacterial β-glucuronidase activity (left panel) and the dietary inhibition of cardiac drug inactivation by Eggerthella lenta (right panel). C. Microbiome-based diagnostics. Examples include measuring: the abundance of bacterial species that are associated with tacrolimus efficacy (left panel); the presence or absence of genes that are associated with the bioavailability of digoxin (middle panel); and the levels of the microbial metabolite p-cresol, which is associated with acetaminophen metabolism (right panel).