Fig. 1.
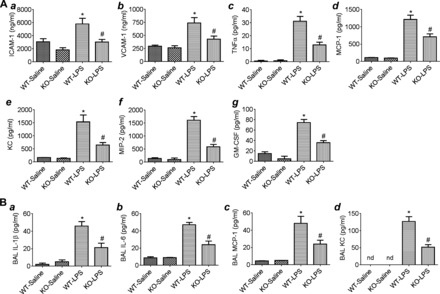
Effect of phospholipase C-ε (PLC-ε) deficiency on LPS-induced proinflammatory mediators in the lung. Age-matched C57BL/6L wild-type (WT) and PLC-ε−/− (knockout, KO) mice were aerosolized with saline alone or saline containing Escherichia coli LPS as described in materials and methods. At 18 h after LPS inhalation, lungs and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluids from these mice were collected, and levels of proinflammatory mediators were measured. A: lung homogenates were analyzed for ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 (a and b) levels by ELISA and TNF-α, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), keratinocyte-derived cytokine (KC), macrophage inflammatory protein 2 (MIP2), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) levels (c–g) by multiplex immune assay system. B: BAL fluids were analyzed for IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, and KC levels (a–d) by ELISA. Data are means ± SE (n = 3–5 for each condition). *P <0.05 vs. saline WT; #P vs. LPS WT. nd, not detected.
