Figure 6.
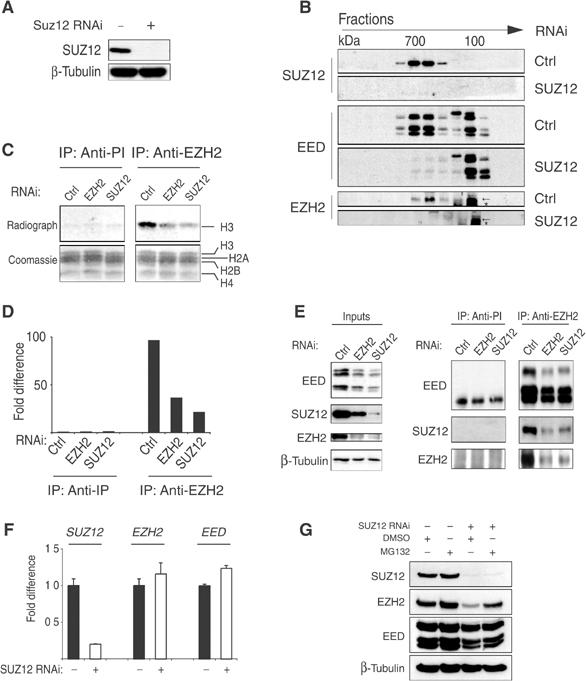
SUZ12 is required for the formation and the HMT activity of EZH2-containing complexes. (A) WB analysis of transiently interfered HeLa cells with control (Ctrl) and SUZ12 siRNA oligos. (B) WB analysis on gel filtration fractions of transiently interfered HeLa cells presented in (A) showing the elution profile of SUZ12, EED and EZH2 in the presence or absence of SUZ12. The arrows indicate EZH2. The asterisk indicates a crossreacting protein recognized by the antibody. (C) HMT assays of IP products of preimmune (anti-PI) and anti-EZH2 serum of transiently interfered HeLa cells with Ctrl, EZH2 and SUZ12 oligos. The bottom panels show the Coomassie staining of the histones used as substrates in the reaction. In the top panel is presented the autoradiograph of the same histones showing the specific H3 HMT of the PRC2 complex and the reduction in activity upon loss of EZH2 and SUZ12. (D) Quantification of the HMT activity presented in (C) by in silico analysis. (E) WB analysis of SUZ12, EZH2 and EED proteins of the experiment presented in (C, D). (F) Expression levels of SUZ12, EZH2 and EED mRNA showing that loss of SUZ12 has no effect on EZH2 and EED expression. (G) WB analysis of transiently interfered HeLa cells with Ctrl and SUZ12 siRNA oligos treated with carrier (DMSO) or 5 μM MG132 proteosome inhibitor for 10 h before harvesting, showing that SUZ12 loss induces a proteosome-dependent degradation of EZH2.
