Figure 2.
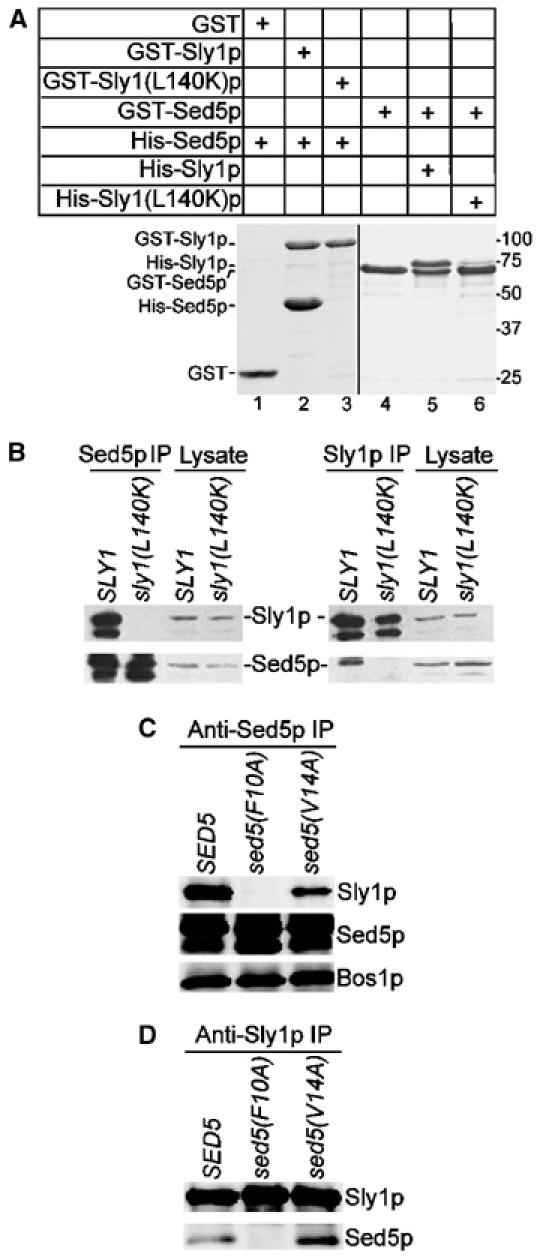
Sly1(L140K)p unable to bind Sed5p, or Sed5(F10A)p abolishing Sly1p binding is functional. (A) Full-length wild-type Sly1p, mutant Sly1(L140K)p and Sed5p fused to GST were immobilized on glutathione–Sepharose beads and incubated with His-tagged Sed5p (0.8 μg/μl), Sly1p (0.8 μg/μl) or Sly1(L140K)p (0.8 μg/μl), respectively. GST fusion proteins and protein complexes formed on beads were analyzed by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. (B) Detergent lysates prepared from yeast strains expressing wild-type Sly1p (strain MSUC3D) and Sly1(L140K)p (strain RPY238) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with affinity-purified anti-Sed5p or anti-Sly1p antibodies. The immunoprecipitates along with a fraction of original lysates (2%) were analyzed on immunoblots. Note that both Sly1p and Sed5p were partially degraded. (C, D) Detergent lysates prepared from cells expressing wild-type Sed5p (strain RPY214), Sed5(F10A)p (strain RPY215) or Sed5(V14A)p (strain RPY216) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Sed5p and anti-Sly1p antibodies as in (B). Proteins co-precipitated with Sed5p or Sly1p were analyzed on immunoblots with antibodies indicated to the right.
